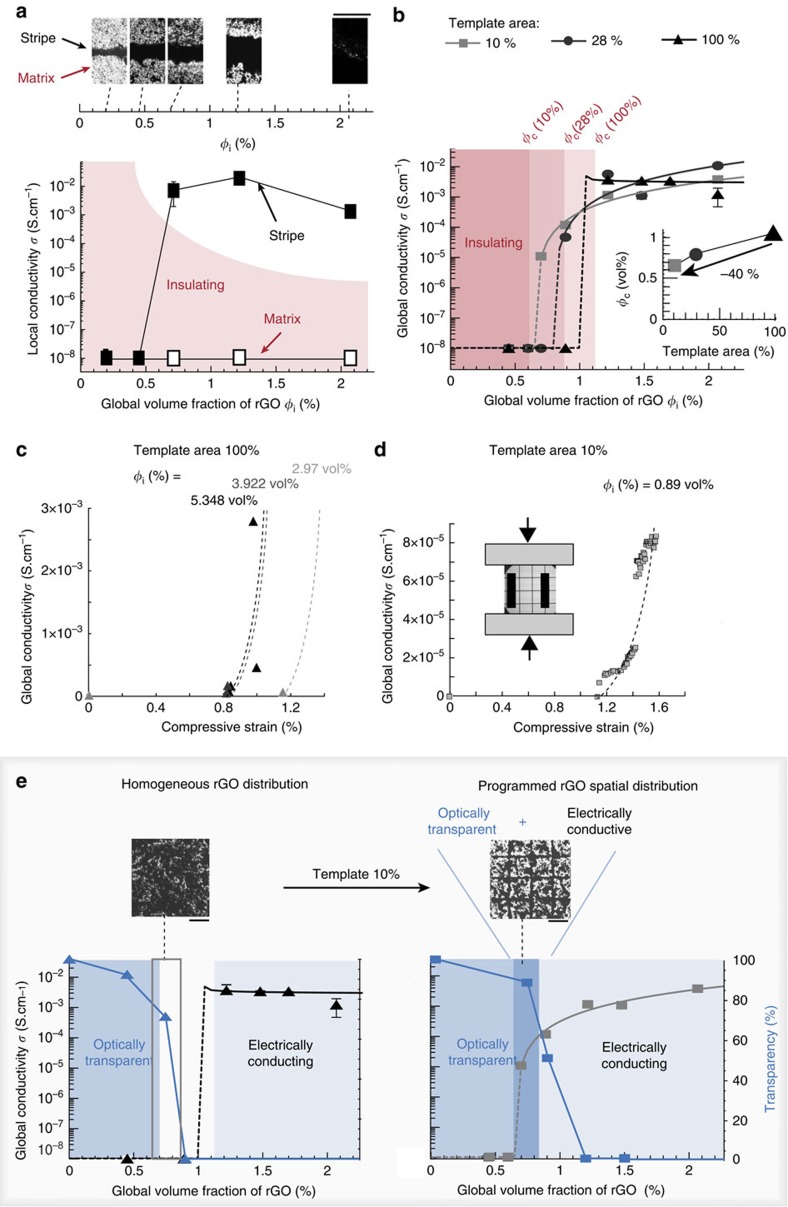
Figure 4. Electric response and transparency of gelatin composite films with magnetically driven percolation threshold.
(a) Optical micrographs (Scale bar, 500 μm) and electrical conductivity measurements demonstrating the local control over electrical conductivity by assembling a volume fraction ϕi (vol%) of m-rGO flakes into a stripe in gelatin composite films (one hierarchical level). (b) Reduction of the percolation threshold ϕc as a function of the mould's template area in gelatin composite films (two hierarchical levels). Experimental global conductivity points are fitted with equation (1). (c,d) Evolution of the global conductivity under compressive strain for composite films prepared with a magnetic template area of 100% and 10%, respectively. The dotted lines are guides to the eyes underlining the trend. The inset in d shows a schematic drawing of the set-up, indicating the direction of the pattern and measuring electrodes relative to the applied force. (e) Controlling the rGO spatial distribution using a magnetic template of 10% area leads to transparent and electrically conductive gelatin films (dark blue region, right) of otherwise opaque and insulating homogeneous films for rGO global volume fractions of 0.65–0.85 vol% (region framed in grey, left). The optical micrographs were obtained from gelatin films containing 0.75 vol% rGO (Scale bar, 500 μm).