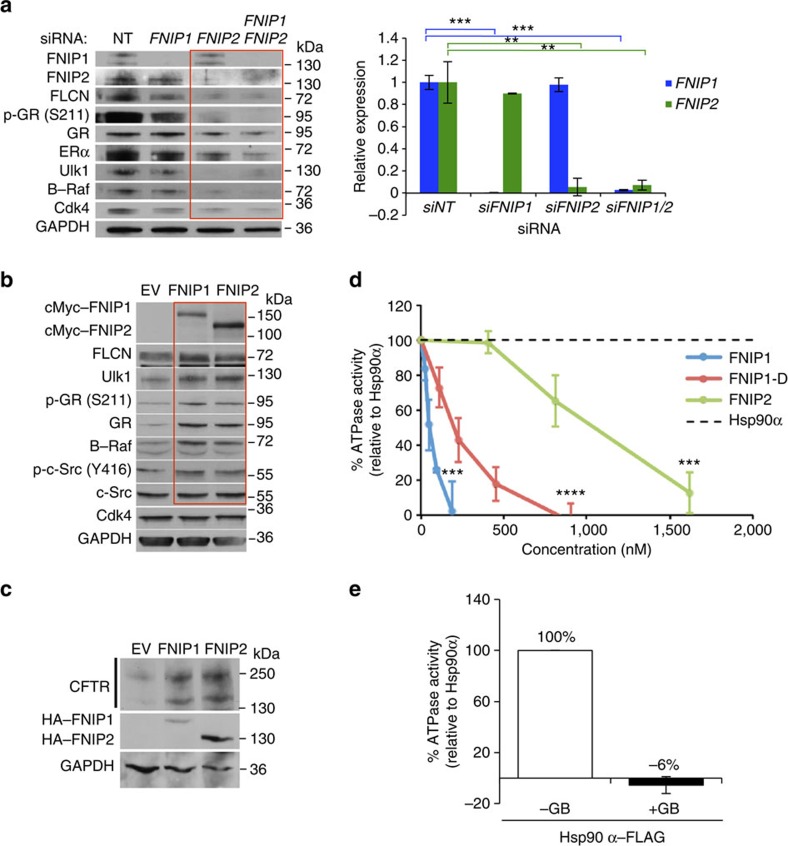
Figure 4. FNIPs co-chaperones inhibit Hsp90 chaperone cycle and facilitate chaperoning of the clients.
(a) Effect of siRNA knockdown of FNIP1 and FNIP2 on Hsp90 clients. Stability and activity of the indicated clients were assessed by immunoblotting. Densitometry of the western blotting for FNIP1 and FNIP2 is represented as mean±s.d. A Student's t-test was performed to assess statistical significance (**P<0.005 and ***P<0.0005). (b) Transient overexpression of cMyc-tagged FNIP1 or FNIP2 in HEK293 cells and their impact on levels of Hsp90 clients was assessed by immunoblotting. Empty vector (EV) was used as a control. (c) HEK293 cells were co-transfected with CFTR and indicated HA–FNIP1 and HA–FNIP2 constructs. After 24 h, CFTR and FNIPs–HA were detected by immunoblotting; GAPDH was used as loading control. Empty vector (EV) was used as a control. (d) In vitro ATPase activity of Hsp90α–FLAG isolated from PC3 cells. Inhibitory effects of purified HA–FNIP1, FNIP1-D–HA or HA–FNIP2 on ATPase activity of Hsp90α–FLAG. All the data represent mean±s.d. A Student's t-test was performed to assess statistical significance (***P<0.0005 and ****P<0.0001). (e) ATPase activity of Hsp90α–FLAG from d was inhibited by addition of 10 μM GB. All the data represent mean±s.d. A Student's t-test was performed to assess statistical significance (****P<0.0001).