Figure 1.
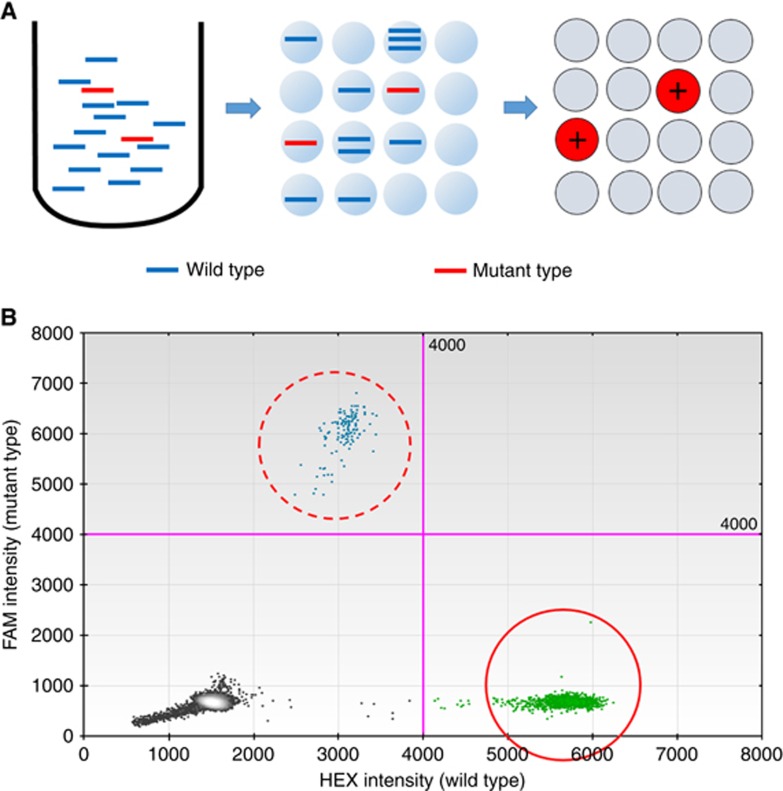
Overview of droplet digital PCR assay.(A) Schematic representation of the droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) assay, which is based on nanolitre-sized water-in-oil emulsion droplet technology. In this assay, target DNA molecules are uniformly distributed across thousands of emulsified droplets, after which PCR amplification is performed in each partitioned droplet. After amplification, reactions containing one or more target DNA molecules represent the positive end-point, whereas those without target DNA molecules represent the negative end-point. The number of target DNA molecules present can be calculated from the fraction of positive end-point reactions using Poisson statistics. (B) Two-dimensional histogram of ddPCR assay for KRAS amplification. FAM (blue) and HEX (green) fluorescence levels were plotted for each droplet. Clusters in the upper and right halves of the plot (dashed circle and solid circle) represent the positive mutant and wild-type KRAS end-point results, respectively.