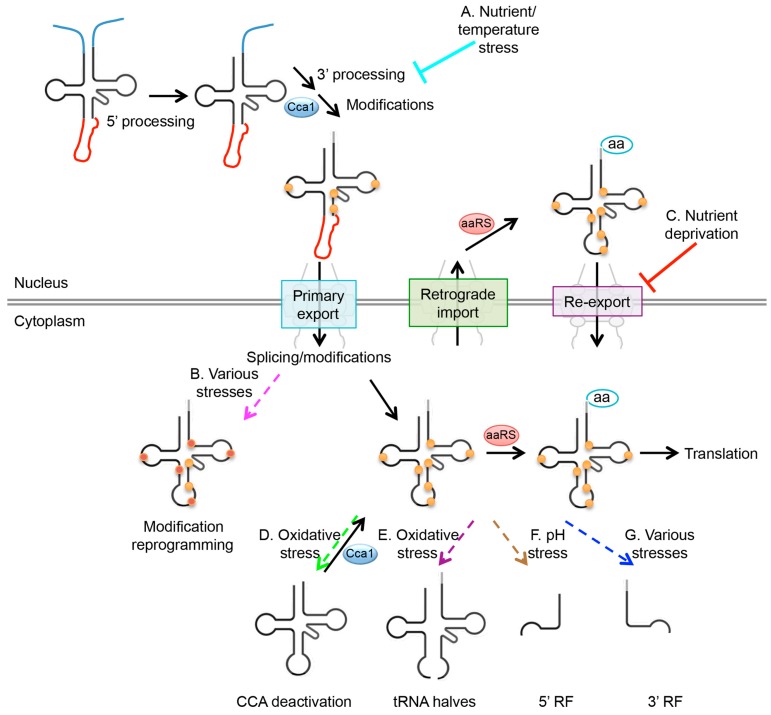
Figure 1.
Stress-induced regulation in tRNA biology. The canonical tRNA biogenesis pathway and subcellular traffic are indicated with solid black arrows. (A) Upon nutrient and/or temperature stress, 3′ trailer sequence processing is likely inhibited and thus aberrant pre-tRNAs accumulate (Cyan blunt-ending line); (B) tRNA modification is subject to change under certain cellular conditions (Magenta dotted arrow); (C) Upon nutrient deprivation, tRNA re-export step is likely inhibited by multiple mechanisms and thus tRNAs accumulate in the nucleus (Red blunt-ending line); (D) Upon oxidative stress, tRNAs are endonucleolytically cleaved within their 3′ CCA termini (Green dotted arrow). Oxidative stress-induced deactivation of the 3′ CCA termini is a dynamically reversible process; (E) When tRNAs are exposed to oxidative stress, heat shock, and UV irradiation, mature tRNAs are endonucleolytically cleaved in the anticodon loops, generating 5′ and 3′ tRNA halves (Purple dotted arrow); (F) The 5′ tRFs are derived from the 5′ parts of mature tRNAs and are formed by a cleavage in the D loop. 5′ tRF can be formed when cells are grown at high pH environment (Brown dotted arrow); (G) 3′ CCA tRFs correspond to 3′ parts of mature tRNAs containing processed 3′ CCA termini and are formed by cleavage at the T loop (Blue dotted arrow). Dicer, angiogenin, and other RNase A family members have been implicated in the generation of the 3′ tRF.