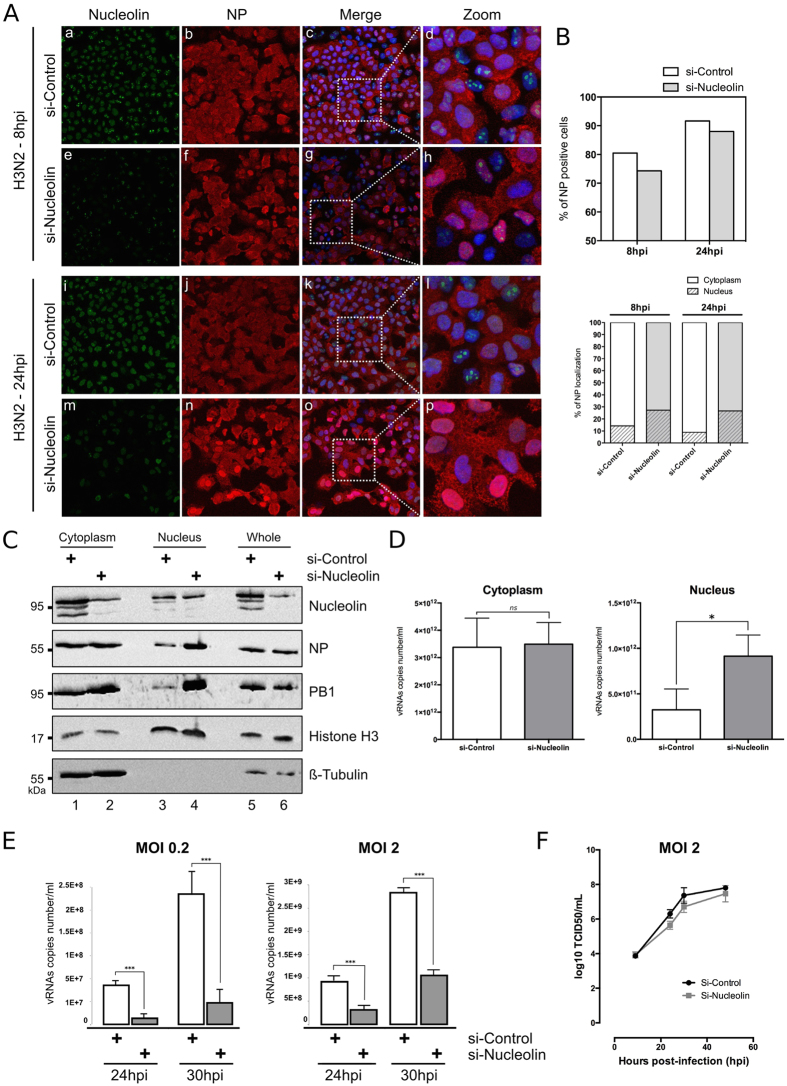
Figure 4. Silencing of endogenous nucleolin alters the nucleocytoplasmic export of vRNPs and decreases the virus production yield.
(A) A549 cells were transfected with either nucleolin (si-Nucleolin, panels e–h and panels m–p) or control (si-Control, panels a–d and panels i–l) siRNAs. Two days after transfection, cells were infected with H3N2 for 8 h or 24 h and immunostained with anti-nucleolin (green) and anti-NP (red) antibodies. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Panels (c,g,k,o) are merged confocal images. Details of cell are enlarged (inset d,h,l,p). (B) Percentage of infection was quantified in si-transfected cells (upper panel). Intranuclear localization of NP was evaluated by counting cells harboring nuclear and/or cytoplasmic labeling in a total of 100 cells per condition, on a total of three distinct fields (lower panel). (C,D) A549 cells were transfected with si-Nucleolin or si-Control and infected with H3N2 virus, as in A and submitted to nucleocytoplasmic fractionation. Equal amounts of proteins from each fraction were analyzed by western blot (C). NP and PB1 proteins were detected using specific antibodies. H3 and β-tubulin were detected as loading and fractionation controls. (D) Total RNAs were extracted from cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions and vRNAs were quantified by specific RT-qPCR (M vRNAs copies number/mL), *P-value <0.05. (E) A549 cells were transfected with si-Nucleolin or si-Control. Two days after transfection, cells were infected with H3N2 at MOI 0.2 and 2 for 24 to 30 hpi. Viral RNAs were extracted from culture supernatants and quantified by RTqPCR, using specific primers for M segment. ***P-value <0.001. (F) A549 cells treated by si-Control or si-Nucleolin (as previously described) were infected with viruses at a MOI of 2. Samples of supernatants were harvested at several time points post-infection and stored at −80 °C until end point viral titration assays in MDCK cells using the Reed and Muench statistical method (TCID50/mL).