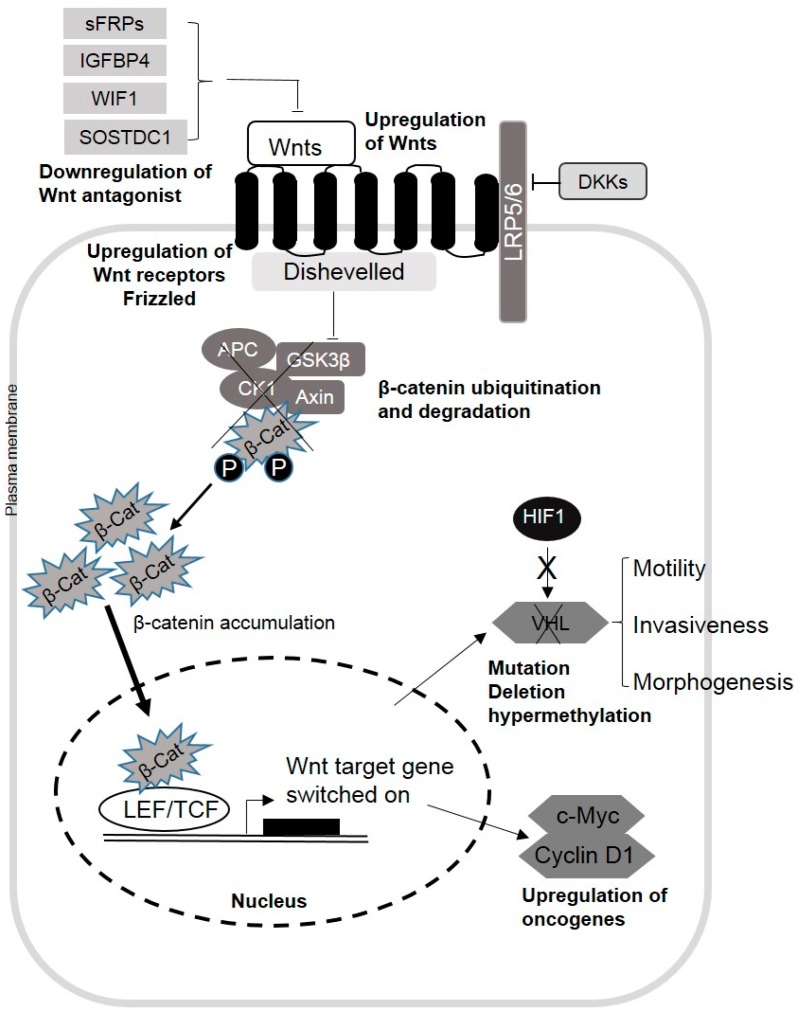
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Wnts binding to its receptors from the Frizzled family stimulates the canonical signaling pathway. The downregulation of Wnts and its co-receptor LRP5/6 antagonists by gene mutation, deletion and promotor hypermethylation also induces the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in RCC. Upon the activation of the pathway, GSK3 kinase activity is inhibited, and the destruction complex becomes disrupted. This allows β-catenin accumulation in the cytoplasm and its localization to the nucleus, which activates Wnts target genes’ transcription. Upregulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway increased the expression of the oncogenes in RCC, such as c-Myc and Cyclin D1. The VHL/HIF pathway is regulated by the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in RCC. The tumor suppressor gene VHL can be silenced by mutation, deletion and promotor hypermethylation. LRP5/6: LDL receptor-related proteins 5 and 6; GSK3: glycogen synthase kinase 3; TCF/LEF: T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancing factor; VHL: von Hippel-Lindau.