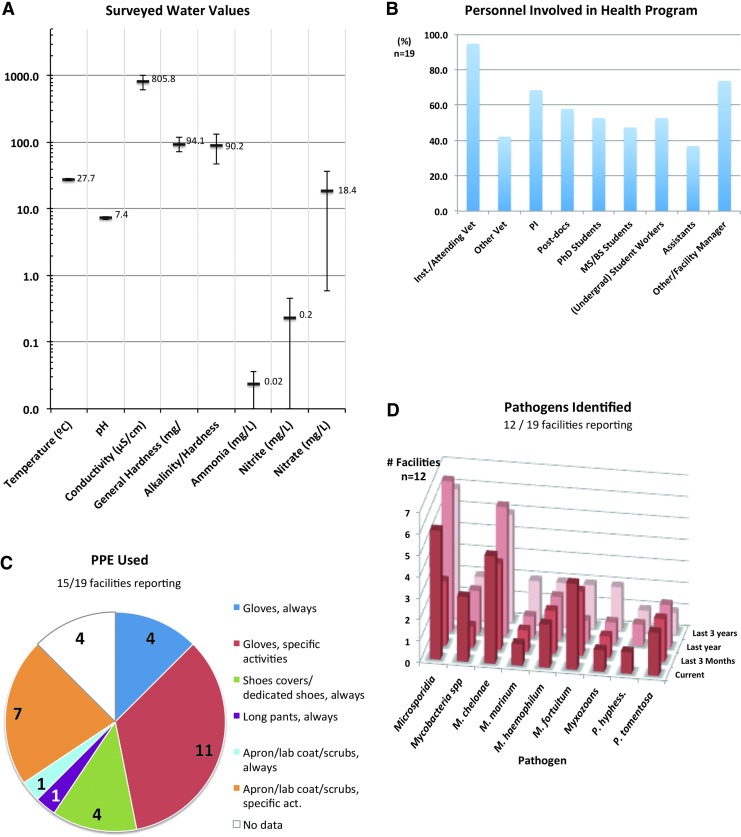
FIG. 1.
Summary of husbandry and health-monitoring program elements. (A) Average water quality values, with upper and lower range. Temperature, pH, and water conductivity were monitored in all 19 facilities [100% in (A)]. The lines indicate average values, the upper bar delineates the average upper range, and the lower bar the average lower range. Temperature (n = 19): 27.7°C (average), 26.5°C (lower range), and (28.8°C upper range); pH (n = 19): 7.4 (average), 7.0 (lower), and 7.8 (upper range); conductivity (n = 19): 805.8, 604.7, and 1006.8 μS/cm; general water hardness (n = 14): 94.1, 71.3, and 116.9 mg/L (concentration of divalent metal ions, e.g., Ca2+, Mg2+); total hardness/alkalinity (n = 5): 90.2, 47.3, and 133.1 mg/L CaCO3; ammonia (n = 17): 0.0232, 0, and 0.0463 mg/L; nitrites (n = 16): 0.2, 0, 0.5 mg/L; nitrates (n = 16): 18.4, 0.6, and 36.2 mg/L. (B) A range of institutional and laboratory personnel is involved in zebrafish care. The chart shows the percentage of the surveyed facilities reporting participation of various institutional and laboratory personnel in animal health. (C) PPE worn. Numbers in the pie indicate how many surveys reported the use of a particular PPE. We distinguished all activities and specific activities as indicated by the colors in the pie chart legend. (D) The number of surveys reporting one or several pathogens in their facility at present, during the past 3 months, during the past year, and during the past 3 years. The microsporidian Pseudoloma neurophilia and Mycobacterium chelonae are most frequently reported. PPE, personal protective equipment.