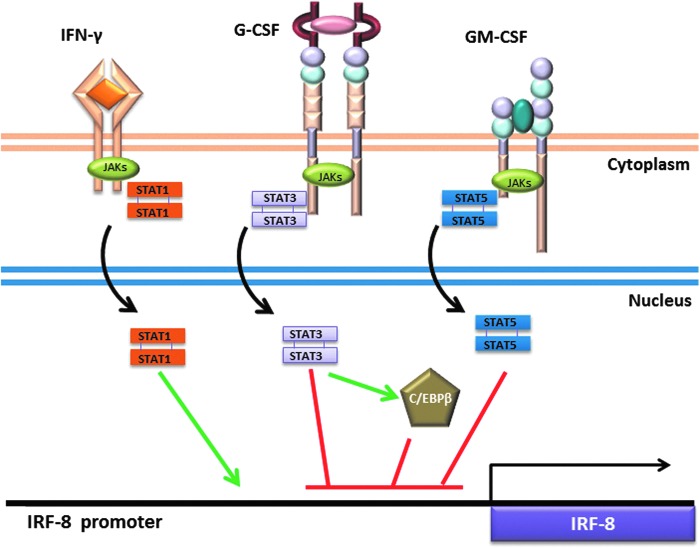
FIG. 2.
Signaling pathways regulating IRF-8 expression. Cytokines signal through engagement of specific cell surface receptors on myeloid populations. The major pathways discussed are highlighted, which illustrate the ability of IFN-γ to induce IRF-8 (green line), or G-CSF or GM-CSF to suppress IRF-8 (red lines) expression. The green or red lines shown in the nucleus are used to simply illustrate the concept that the different transcription factors inhibit IRF-8 transcription, not necessarily the precise location of their binding elements within the IRF-8 promoter. STATs are activated by phosphorylation by JAKs and subsequent translocation into the nucleus (black arrows). STAT3 induces (green arrows) the transcription factor C/EBPβ, which may also negatively regulate IRF-8 (at least in DC biology). In addition, cytokine signaling induces mechanisms of feedback inhibition, such as regulation of STAT1 by SOCS1, STAT3 by SOCS3, or STAT5 by SOCS2 (not shown).