Fig. (3).
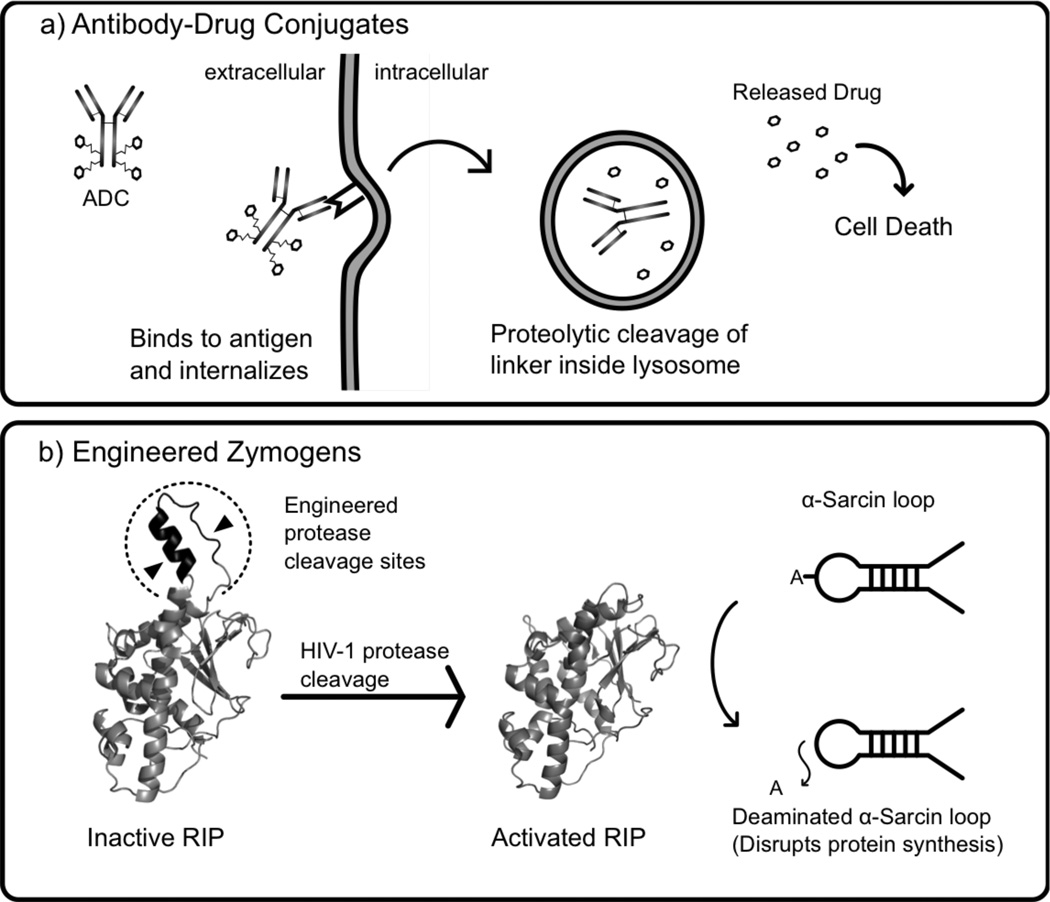
Illustrations of select classes of protein therapeutics engineered for targeted drug activation. A) Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are composed of a monoclonal antibody securely linked to several molecules of a cytotoxic drug. The antibody selectively binds to a receptor on a cancer cell and is internalized via receptor mediated endocytosis. Once delivered to a lysosome, the linker is proteolytically cut and the drug is released leading to cell death [45, 137]. B) Engineered zymogens are proteins which have been engineered to be in an inactive state until activated by a specific signal, such as proteolytic cleavage. Law et al. engineered a zymogen variant of maize ribosome-inactivating protein (RIP) (represented by PDB code 2PQG) which is activated by HIV-1 protease for anti-HIV therapy [56]. Once activated, maize RIP (PDB code 2PQI) removes an adenine from the α-sarcin site on the large (28S) ribosomal subunit, disrupting protein synthesis [138].