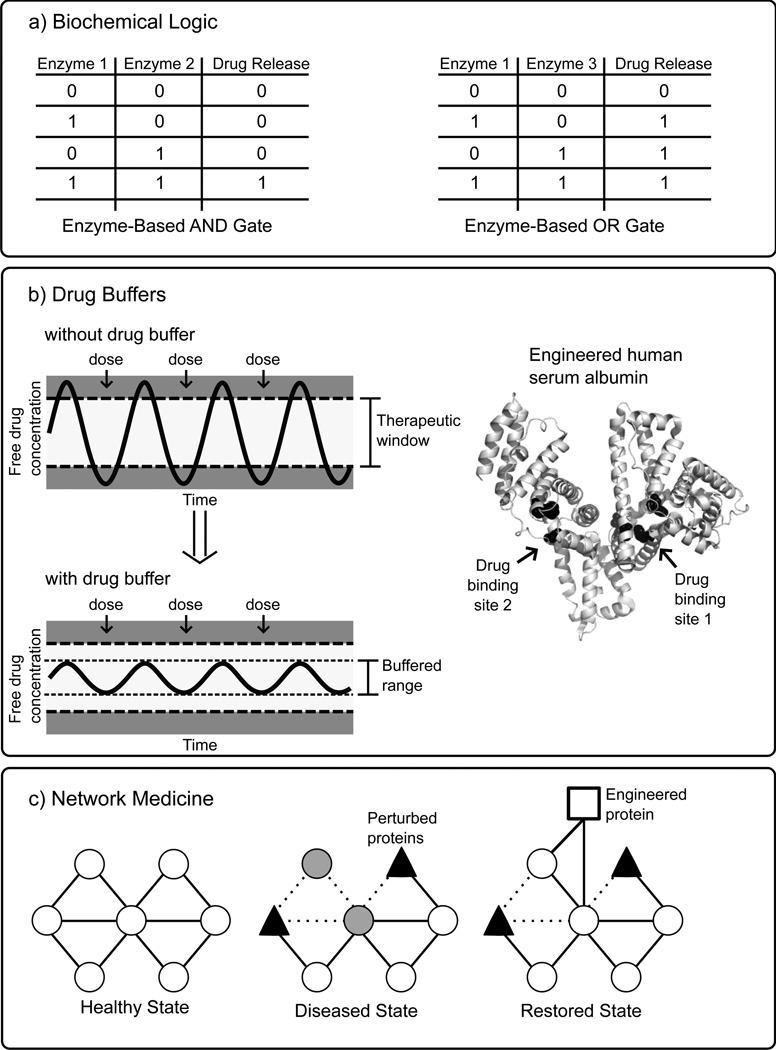
Fig. (6).
Illustrations of protein engineering enabled smart response drug systems. A) Stimulus-responsive delayed release drug systems have been proposed which utilize combinations of enzymes which can integrate multiple inputs according to biochemical (typically Boolean) logic to release an appropriate amount of one or several drugs under specified conditions [106]. B) A drug buffer is an engineered multivalent ligand-binding protein therapeutic which has been designed to bind or release a narrow therapeutic window drug in such a manner that the free drug concentration is maintained within a safe and effective range. For illustrative purposes, human serum albumin (PDB code 1O9X) is shown with potential engineered drug binding sites at Sudlow’s site 1 and site 2 (black spheres) [116]. C) Network medicine is new therapeutic approach which aims to restore health by targeting and correcting aberrant signaling networks associated with cancer and other diseases. In this highly simplified schematic, a disease state is the result of perturbed proteins which disrupt the organization of the healthy signaling network. The introduction of an engineered signaling protein “re-wires” the network around the perturbed proteins, restoring health.