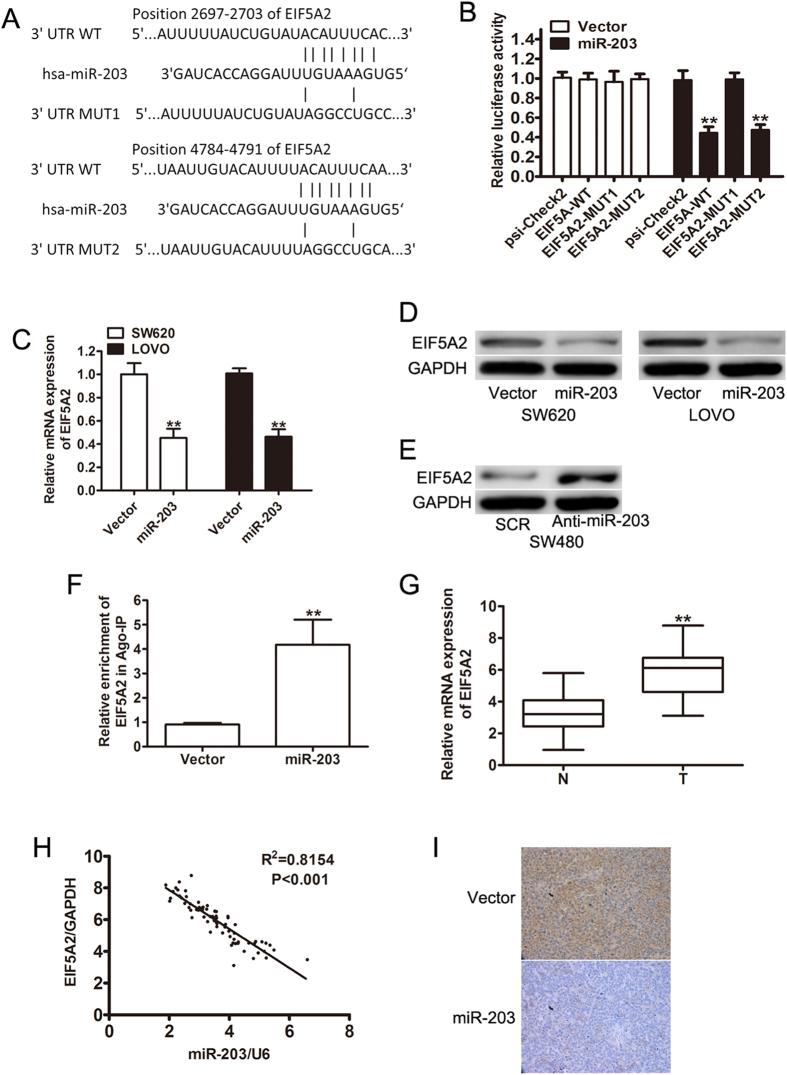
Figure 5. miR-203 directly targets EIF5A2.
(A) The putative miR-203-binding sequence in the 3′UTR of the EIF5A2 mRNA is shown. A mutation was generated in the EIF5A2 3′UTR sequence at the complementary site for the seed region of miR-203. (B) The luciferase reporter assays show reporter activity after co-transfection of either EIF5A2-3′-UTR or mutant 3′UTRs of EIF5A2 with miR-203 in the HEK-293 cells (**P < 0.01). (C,D) The re-expression of miR-203 in the SW620 and LOVO cells attenuated the expression of EIF5A2 mRNA and protein levels, respectively. (E) A western blot analysis of the relative protein levels of EIF5A2 in the miR-203 inhibitor and control inhibitor groups in the SW480 cell lines. (F) RIP-IP assays were performed to co-IP the Ago2 complexes from the LOVO cells transfected with the control or miR-203. The relative enrichment of the EIF5A2 mRNA from the Ago2 co-IP fractions was detected by qRT-PCR assays. (G) The relative level of EIF5A2 mRNA in 72 pairs of CRC and adjacent nontumor mucosa tissues. (H) A Spearman Correlation analysis clearly shows a negative correlation between miR-203 and EIF5A2 mRNA expression in the CRC tissues (P < 0.001). (I) The IHC staining shows EIF5A2 in the tumor samples from the LOVO-vector and LOVO-miR-203 cells. **p < 0.01.