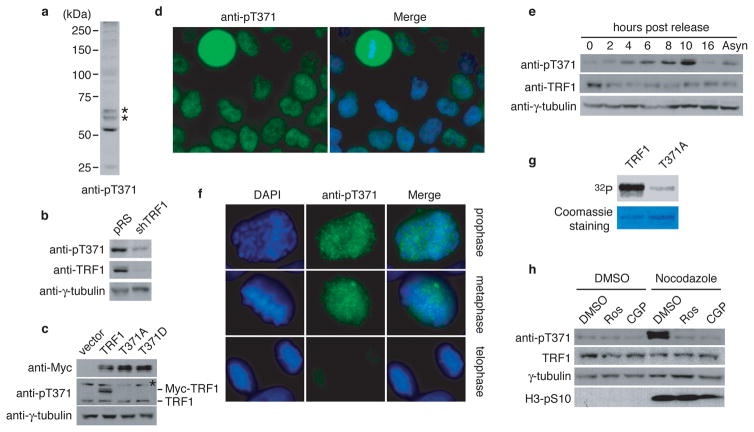
Figure 1. T371 of TRF1 is phosphorylated in early mitosis.
(a) Western analysis with anti-pT371 antibody. Asterisks indicate non-specific bands that do not respond to shTRF1 knockdown. (b) Western analysis of HeLaII cells depleted for endogenous TRF1. Immunoblotting was performed with anti-pT371 or anti-TRF1 antibody. The γ-tubulin blot was used as a loading control in this experiment and all following westerns shown in this article. (c) Western analysis of various Myc-tagged TRF1 proteins as indicated. Immunoblotting was performed with anti-Myc, anti-pT371 or anti-γ-tubulin antibody. Myc-tagged TRF1 proteins migrate slower than endogenous TRF1. Asterisks indicate non-specific bands that do not respond to shTRF1 knockdown. (d) Indirect immunofluorescence with anti-pT371 antibody on transformed GM637 cells. (e) Western analysis of cell extracts from asynchronous HeLaI.2.11 cells (Asyn) or cells released for 0–16 h from a double thymidine block. (f) Indirect immunofluorescence with anti-pT371 antibody on HeLaI.2.11 cells. (g) In vitro Cdk1 kinase assays. Recombinant cyclin B-Cdk1 was incubated with bacteria-expressed his-tagged wild type TRF1 or TRF1 mutant T371A in the presence of γ-32P-ATP. (h) Western analysis. HeLaI.2.11 cells were treated with either DMSO or nocodazole, followed by incubation with or without Cdk1 inhibitors Roscovitine (Ros) or CGP74514A (CGP). Immunoblotting was performed with anti-pT371, anti-TRF1, anti-H3pS10 or anti-γ-tubulin antibody.