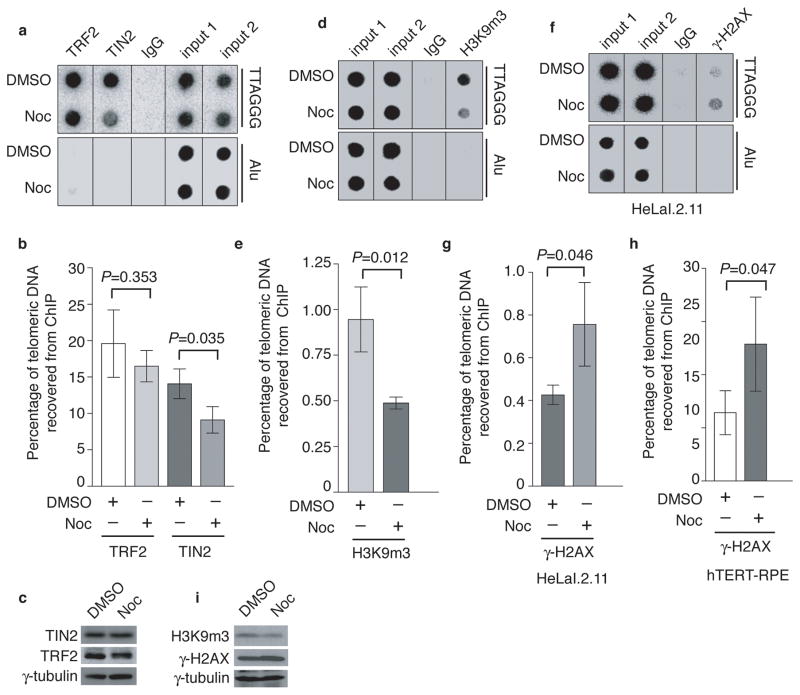
Figure 4. Nocodazole arrest results in loss of TIN2 and the heterochromatic mark at telomeres and an accumulation of γ-H2AX at telomeres.
(a) Dot blots of anti-TIN2 and anti-TRF2 ChIPs from HeLaI.2.11 cells treated with either DMSO or nocodazole. (b) Quantification of anti-TRF2 and anti-TIN2 ChIPs from (a). The P value was calculated using a Student’s two-tailed t test. Standard deviations from three independent experiments are indicated. (c) Western analysis with anti-TIN2, anti-TRF2 or anti-γ-tubulin antibody. (d) Dot blots of anti-H3K9m3 ChIPs from HeLaI.2.11 cells treated with either DMSO or nocodazole. (e) Quantification of anti-H3K9m3 ChIPs. The P value was calculated using a Student’s two-tailed t test. Standard deviations from three independent experiments are indicated. (f) Dot blots of anti-γ-H2AX ChIPs from HeLaI.2.11 cells treated with either DMSO or nocodazole. (g) Quantification of anti-γ-H2AX ChIPs from (f). The P value was calculated using a Student’s two-tailed t test. Standard deviations from three independent experiments are indicated. (h) Quantification of anti-γ-H2AX ChIPs for hTERT-RPE cells. The P value was calculated using a Student’s two-tailed t test. Standard deviations from three independent experiments are indicated. (i) Western analysis with anti-H3K9m3, anti-γ-H2AX or anti-γ-tubulin antibody.