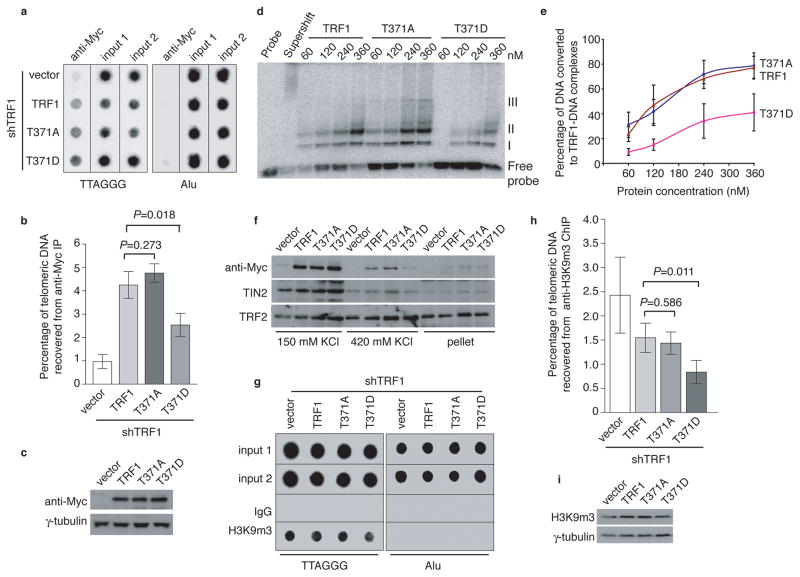
Figure 6. Phosphomimic mutation at T371 (T371D) impairs TRF1 interaction with telomeres and promotes loss of telomere heterochromatin.
(a) Dot blots of anti-Myc ChIPs from TRF1-depleted HeLaII cells expressing various constructs as indicated on the left. (b) Quantification of anti-Myc ChIPs from (a). The P values were calculated using a Student’s two-tailed t test. Standard deviations from three independent experiments are indicated. (c) Western analysis of Myc-tagged TRF1 proteins. (d) In vitro gel shift assays. Bacteria-derived recombinant TRF1 proteins were used in the gel-shift assays as indicated above the lanes. The positions of three TRF1-containing complexes (I, II and III) are indicated on the right. All TRF1-containing complexes can be supershifted by anti-TRF1 antibody. The concentrations of recombinant TRF1 used were indicated above the lanes. (e) Quantification of percentage of total DNA converted to TRF1-DNA complexes. Standard deviations for TRF1 mutants (T371A and T371D) were derived from three independent experiments whereas standard deviations for wild type TRF1 were derived from at least two independent experiments. (f) Differential salt extraction of chromatin on TRF1-depleted cells expressing various constructs as indicated above the lanes. (g) Dot blots of anti-H3K9m3 ChIPs from TRF1-depleted HeLaII cells expressing various constructs as indicated. (h) Quantification of anti-H3K9m3 ChIPs. The P values were calculated using a Student’s two-tailed t test. Standard deviations derived from four independent experiments are indicated. (i) Western analysis of H3K9m3 expression.