Figure 3. Effect of intraplantar BoNT-B pre-treatment on intraplantar carrageenan induced increase in pAkt and pGluA1 expression.
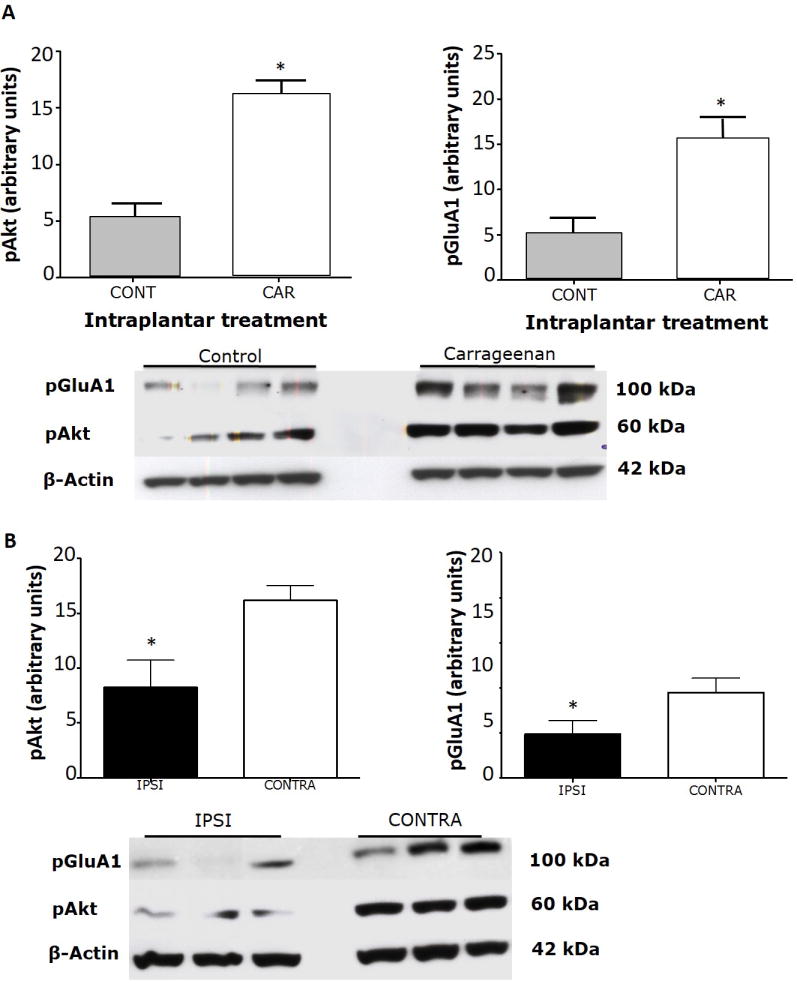
A) Bilateral intraplantar carrageenan (car) induced a significant increase in pAkt and pGluA1 compared to control (cont) in the dorsal half of the lumbar spinal cord. Tissue was sampled 1 h after the carrageenan injection. Histogram depicts the relative expression of pAkt and pGluA1 expression quantified by densitometric measurement. Representative Western blots are shown below the graphs. B) When the experiment was repeated with an i.pl. pre-treatment of BoNT-B in one paw (ipsi) and saline in the other, 2 days prior to the carrageenan injection, the levels of pAkt and pGluA1 in the ipsilateral dorsal quadrant of the spinal cord were significantly suppressed with respect to the saline pre-treated animals. Histogram depicts the relative expression of pAkt and pGluA1 expression quantified by densitometric measurement. Representative Western blots are below each set of graphs. * p≤0.01. Unpaired t-tests. N=4/gp. BoNT-B: botulinum toxin B, pAkt: phosphorylated Akt, pGluA1: phosphorylated GluA1.
