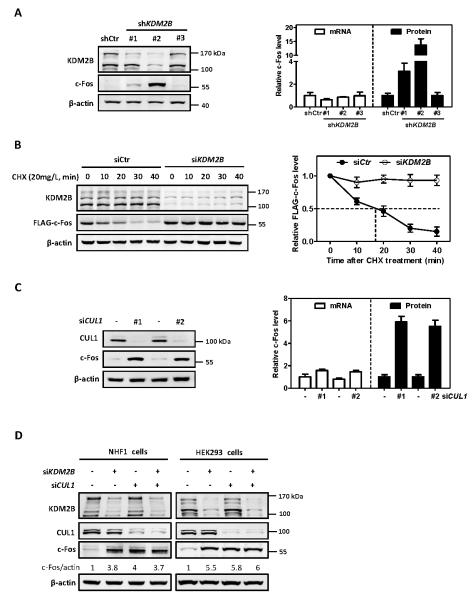
Figure 1. KDM2B/FBXL10 and CUL1 destabilize c-Fos protein.
(A) Stable knock down of KDM2B increases endogenous c-Fos protein level. Two distinct bands of KDM2B (170 KDa and 120 KDa, respectively) were observed in HEK293 cells, representing the two isoforms. The protein and mRNA levels of c-Fos were determined by western blot and qRT-PCR, respectively, and normalized against β-actin. Error bars represent ±SD for triplicate experiments.
(B) Ectopically expressed c-Fos is stabilized by knock down of KDM2B. HEK293 cells stably expressing FLAG-c-Fos were transfected with siRNA oligonucleotides targeting KDM2B or control siRNA. 72 hours after siRNA transfection, the half-life of FLAG-c-Fos protein levels was determined by cycloheximide (CHX, 20 mg/L) chase assay and normalized against β-actin. Error bars represent ±SD for triplicate experiments.
(C) Knock down of CUL1 increases c-Fos protein level. HEK293 cells were transfected with two different siRNAs targeting CUL1 or a control siRNA. 72 h after transfection, the protein and mRNA levels of c-Fos were determined by western blot and qRT-PCR respectively and normalized against β-actin. Error bars represent ±SD for duplicate experiments.
(D) Knock down of either KDM2B or CUL1 or combination increases c-Fos protein to a similar level. NHF1 cells and HEK293 cells were transfected with siRNA oligonucleotides targeting either KDM2B or CUL1 individually or in combination. The protein and mRNA levels of c-Fos were determined by western blot and qRT-PCR, respectively, and normalized against β-actin. Error bars represent ±SD for triplicate experiments.