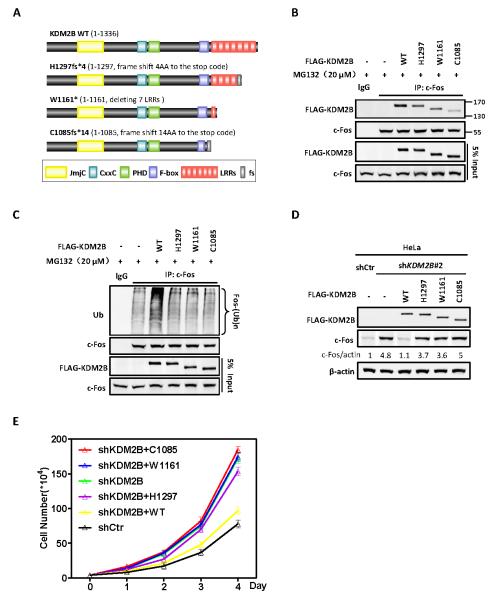
Figure 6. Tumor-derived mutations impair the function of KDM2B/FBXL10 to target c-Fos degradation and suppress cell proliferation.
(A) Schematic representations of three tumor-derived mutants of KDM2B examined in this study. Additional tumor-derived mutations in KDM2B are shown in Figure S6.
(B) Tumor-derived mutations in KDM2B impair their binding to c-Fos. HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing indicated proteins. The interactions between WT or mutant KDM2B and c-Fos were determined by Co-IP.
(C) Tumor-derived mutations in KDM2B impair their ability to ubiquitylate c-fos in vivo. HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing indicated proteins and treated with 20 μM MG132 for 6 h. Endogenous c-Fos was immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted with an antibody specific against ubiquitin.
(D) Tumor-derived mutants of KDM2B abolish their function in promoting c-Fos degradation. HeLa cells with stable knockdown of KDM2B were established by lentivirus transduction. FLAG-tagged wild-type or tumor-derived mutants KDM2B was then stably expressed in these cells. The protein levels of c-Fos were determined by western blot and normalized against β-actin.
(E) Tumor-derived mutations lose the function of KDM2B in suppressing cell proliferation. Sable HeLa cells were identified as in Figure 6D. Cell numbers were counted each day. Error bars represent ±SD for triplicate experiments.