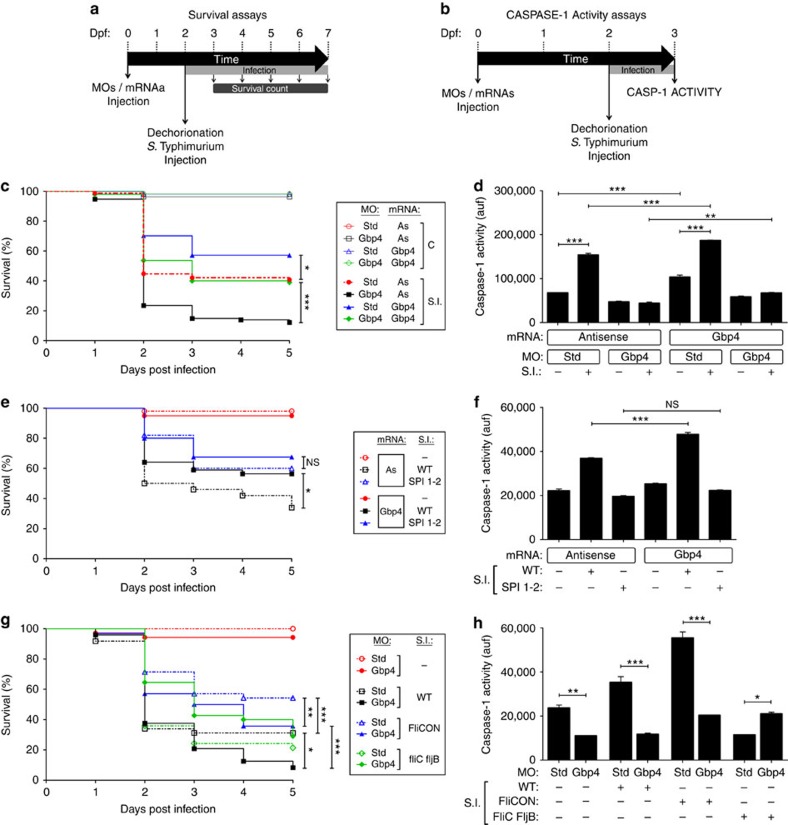
Figure 2. Zebrafish Gbp4 is required for the inflammasome-dependent resistance to S. Typhimurium.
(a) Scheme showing the experimental procedure used for the survival assays. Zebrafish one-cell embryos were injected with MOs and/or mRNAs, dechorionated and infected at 2 dpf via the yolk sac with different strains of ST at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10, and the number of surviving larvae counted daily during the next 5 days. At least 3 independent experiments were performed with a total number of >300 specimens/treatment (actual number indicated in each legend). (b) Scheme showing the experimental procedure used for the caspase-1 activity assays. Zebrafish one-cell embryos were injected with MOs and/or mRNAs, dechorionated and infected at 2 dpf via the yolk sac with different strains of ST with a MOI of 50, and collected 24 hpi and pooled (25–35 larvae) to measure caspase-1 activity. At least three independent experiments were performed and one of them is shown. (c,d) Zebrafish one-cell embryos were injected with standard control (std) or Gbp4 MOs in combination with antisense (As) or Gbp4 mRNAs, infected at 2 dpf with WT ST (d,e), WT and the DM SPI 1–2 (e,f), or (WT), FliCON and FliC FljB (g,h), and the survival (c,e,g) and caspase-1 activity (d,f,h) were determined as described in a and b, respectively. The sample size for each treatment is 325 in c, e and g, 30 in d, f, and h. NS, not significant; SI, ST infection; *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 according to log-rank test (c,e and g) or ANOVA followed by Tukey multiple range test (d,f and h).