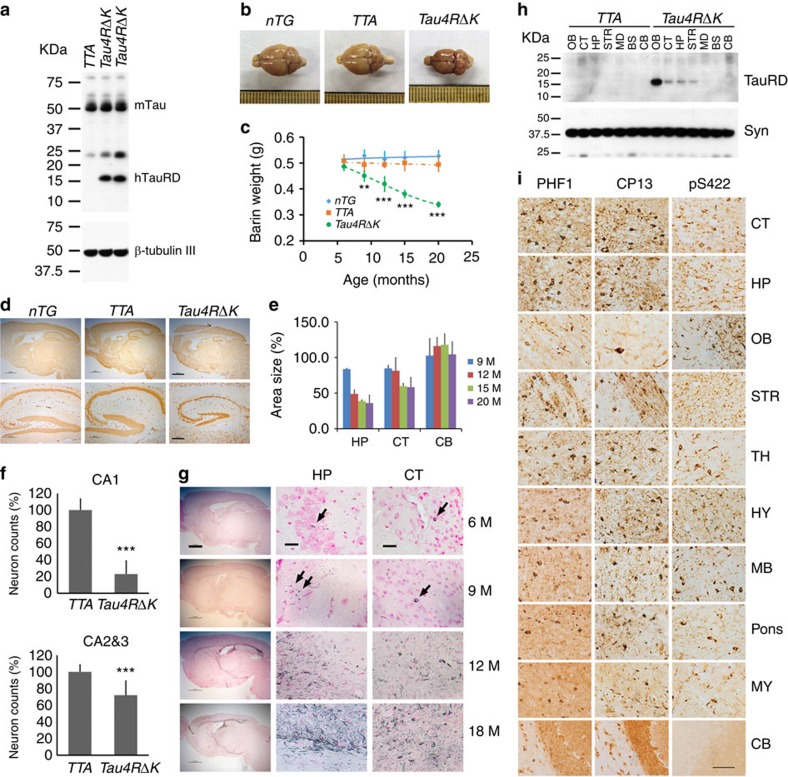
Figure 5. Pathological conversion of tau induced by a mutant tau repeat domain.
(a) Protein blot using 77G7 antibody to detect exogenous (∼16 kDa) TauRDΔK and endogenous tau protein from brain lysates of mutant tau transgenic (Tau4RΔK) mice (n=9). (b) Representative brains of nTG, TTA and Tau4RΔK mice at 20 months of age. Note marked forebrain atrophy in Tau4RΔK mice (n=7). (c) The plot of brain weight of nTG (n=29), TTA (n=27) and Tau4RΔK (n=24) mice at different of ages. The brain weight of Tau4RΔK mice is progressively reduced with aging. (one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), 9 M **P=0.02; 12 M ***P=0.0001; 15 M ***P=0.0003; 20 M ***P=0.0006). (d) Immunohistochemical analysis using antiserum specific to NeuN: sagittal sections (upper panels; scale bar, 1,000 μm) and hippocampi (lower panels; scale bar, 200 μm) of 18-month-old Tau4RΔK (n=8) and control mice (n=15). (e) Sizes of cortical (CT), hippocampal (HP) and cerebellum (CB) regions in brains of Tau4RΔK (n=24) at various ages. Note reduction of hippocampus and cortical region, but not cerebellum in Tau4RΔK mice. (f) Neuronal cell count of CA1 (T-Test, ***P=4.45E−09) and CA2&3 (T-Test, ***P=0.00033) region from 12 months old TTA (n=7), Tau4RΔK (n=7) mice using ImageJ analysis. (g) Gallyas-Braak silver staining of brain sections of Tau4RΔK mice at various ages. The sections were counterstained with fast red. The left panel is overview image of the sagittal section of brains (Scale bar, 1,000 μm). The middle and right panels are hippocampal (HP) and cortical regions (CT). (Scale bar, 25 μm). Tau tangle could first be detected at 6 months of age, and the accumulation of tangles were dramatically increased while aging. (h) Total protein was extracted from different brain regions: olfactory bulb (OB), cortex (CT), hippocampus (HP), striatum (STR), midbrain (MB), brain stem (BS), cerebellum (CE) of 9 months old TTA (n=3) and Tau4RΔK (n=3) mice. Human tau fragment (∼16 kDa) detected using anti-human tau polyclonal antiserum KJ9A was only seen in frontal region, but not in MB, BS or CE. (i) Immunohistochemial analysis of brains of 20 months old Tau4RΔK mice (n=5) by antibodies specific to phosphorylated endogenous tau: PHF-1 (left panel), CP13 (middle panel), and tau-pS422 (right panel), respectively. Scale bar, 50 μm.