Figure 4.
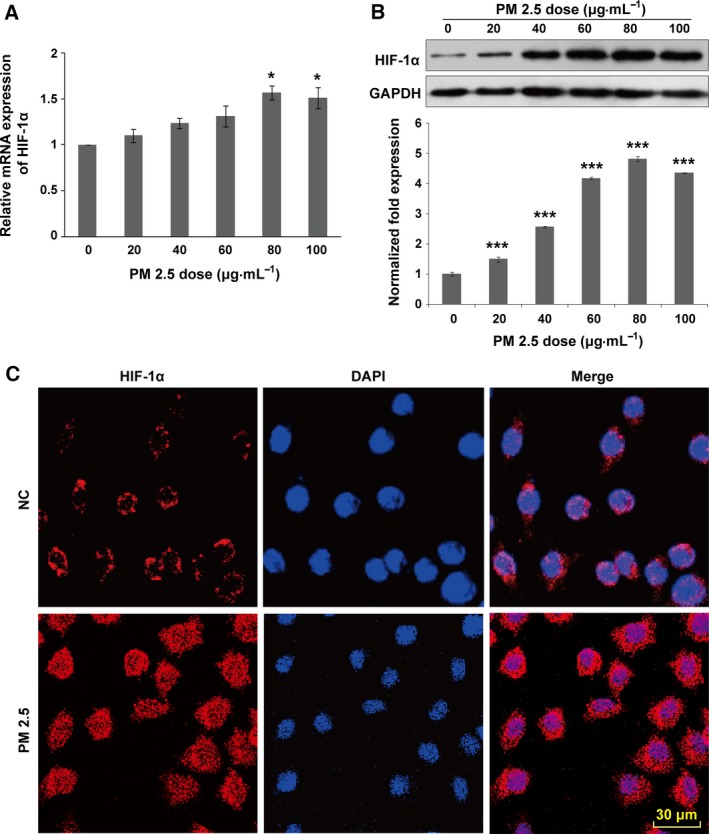
Ambient fine particulate matter increases the transcriptional activity of HIF‐1α in HUVECs. Cells were stimulated with PM2.5 at different concentrations (0, 20, 40, 60, 80, and 100 μg·mL−1) for 24 h. (A) PM2.5 caused a dose‐dependent increase in HIF‐1α mRNA expression. At a PM2.5 concentration of 80 μg·mL−1, HIF‐1α expression peaked at a level ~1.5‐fold higher than that observed in the control (n = 6). (B) HIF‐1α protein expression was analyzed by western blotting. The intensities of the protein bands were quantified and normalized to those of GAPDH. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD. (C) After exposure to PM2.5 (80 μg·mL−1) for 24 h, cells were stained for HIF‐1α by immunofluorescence. Stimulation increased the level of HIF‐1α expression and accumulated within the nucleus. Data are representative of three independent experiments performed in duplicate. Scale bar: 10 μm. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001. Bar: 30 μm.
