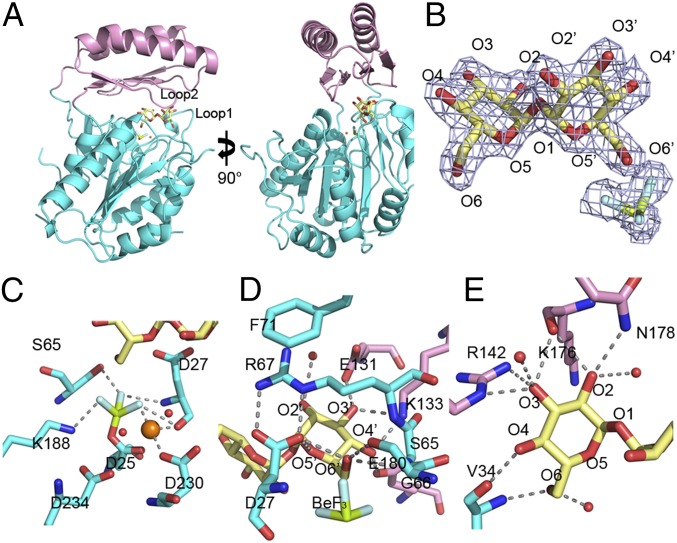
Fig. 3.
Structure of the C. albicans Tps2PD–BeF3–trehalose transition-state complex. (A) Two views of the structure of the Tps2PD–BeF3–trehalose transition-state complex. The core domain and cap domains are shown as cartoons and colored cyan and pink. The trehalose and BeF3 are shown as sticks and the Mg2+ as an orange sphere. (B) A 2Fo-Fc electron density map of the bound trehalose and covalently bound BeF3, shown as light blue mesh and contoured at 1.5 σ. Trehalose is shown as pale yellow sticks. The oxygen atoms are labeled where primed oxygens are found on the glucose ring close to the catalytic residue D25. The beryllium and fluoride are colored olive and light cyan, respectively. (C) View of core-domain residues involved in transition-state stabilization, as depicted by the D25-BeF3 covalent link and Mg2+ ion coordination. The cap-domain residues are shown as atom-colored cyan sticks, and the magnesium ion and waters are depicted as spheres and colored orange and red, respectively. Selected hydrogen bonds are shown by dashed lines. (D) View of residues and solvent involved in binding the catalytic-residue proximal glucose moiety of trehalose. Residues from the cap domain are shown as atom-colored pink sticks and from the core domain as atom-colored cyan sticks. Hydrogen bonds are shown by dashed lines. (E) View of residues and solvent involved in binding the catalytic-residue distal glucose moiety of trehalose. Hydrogen bonds are shown by dashed lines.