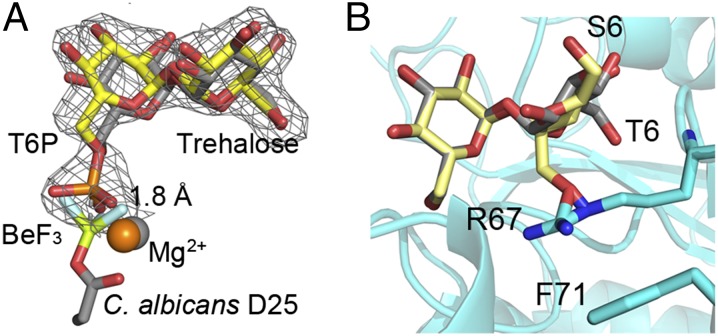
Fig. 4.
Superpositions reveal key steps in catalysis and substrate specificity of Tps2. (A) View of T6P in the C. neoformans Tps2PD(D24N) closed conformation structure after superposition of the protein onto the Tps2 from the C. albicans Tps2–BeF3–trehalose transition-state complex. Note the significant overlap of the T6P and trehalose sugars. T6P from the C. neoformans Tps2PD structure is shown as atom-colored yellow sticks. A 2Fo-Fc electron density map of T6P bound to the C. neoformans Tps2PD is shown as gray mesh and contoured at 1.5 σ. Trehalose and the D25-BeF3 covalent adduct are shown as atom-colored gray sticks. Mg2+ ions from the C. neoformans and C. albicans Tps2PD structure are shown as orange and gray spheres, respectively. (B) Superposition of the glucose moieties of trehalose and sucrose in the C. albicans Tps2PD–BeF3–trehalose–Mg2+ transition-state complex structure. Trehalose and sucrose are shown as atom-colored gray and yellow sticks, respectively. The 6 position of the phosphorylated glucose and fructose moieties of T6P and S6P is labeled as T6 and S6. The side chains of residues R67 and F71 are shown as cyan- and atom-colored sticks.