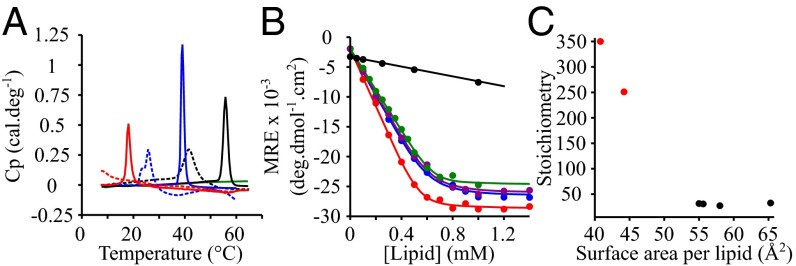
Fig. 2.
Lipid-binding properties of α-synuclein in the presence of model membranes composed of lipids with different chain properties. (A) DSC thermograms of 500 μM DMPS (blue), DLPS (red), DOPS (green), and DPPS (black) in the absence (continuous lines) and presence (dotted lines) of 100 μM α-synuclein. (B) Change in the mean residual ellipticity (MRE) at 222 nm of α-synuclein (20 μM) incubated at 30 °C in the presence of increasing concentrations of DOPS (green), POPS (purple), DLPS (red), DMPS (blue), and DPPS (black). (C) Variation in the number of lipid molecules associated with one molecule of α-synuclein as a function of the surface area of the different lipids. The data points colored in red and black correspond to model membranes in the solid gel and fluid phase, respectively.