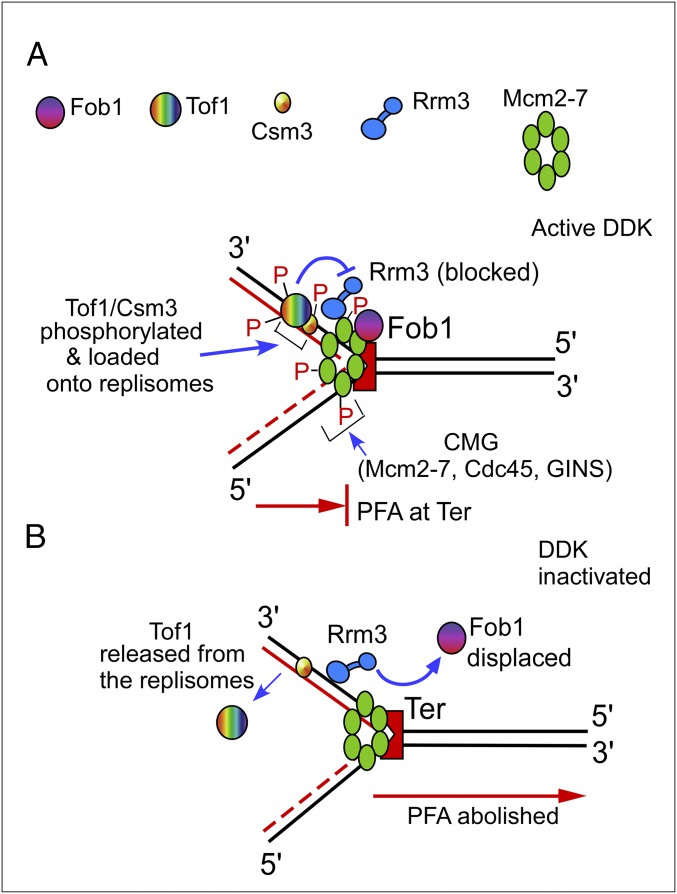
Fig. 6.
Schematic representations of a model illustrating the mechanism of programmed fork arrest. Cdc7, GINS, and Cdc45 are not shown, to simplify the figure. (A) DDK phosphorylates Mcm2–7 and, along with Cdc45 and GINS, assembles CMG, which recruits phosphorylated Tof1–Csm3. Tof1–Csm3 antagonizes Rrm3 to prevent displacement of Fob1 from Ter. (B) In the absence of DDK, Tof1 is no longer maintained at Ter, causing unhindered fork passage. See the text for further details.