Figure 1. Age‐associated impairments in functional sympatholysis .
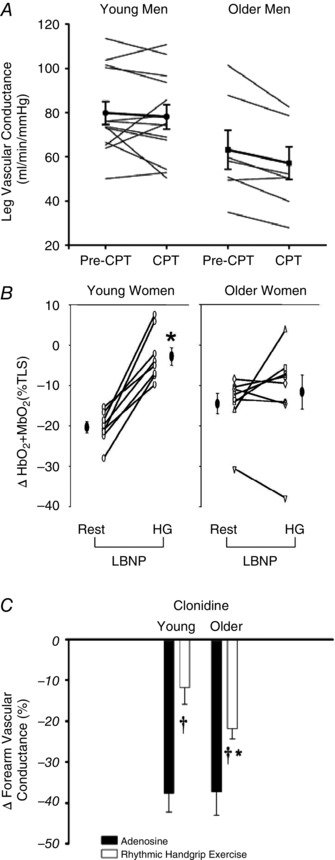
A, sympathetic vasoconstrictor responses to cold pressor test (CPT) during moderate intensity cycle exercise were greater in older relative to young men (%ΔFVC: −14 ± 3% vs. −2 ± 4%, respectively; P < 0.05; FVC: forearm vascular conductance). B, similarly, vasoconstrictor responses (assessed as decreases in skeletal muscle oxygenation) during sympathetic stimulation via lower body negative pressure (LBNP) were not blunted during moderate intensity handgrip exercise compared with resting conditions in older women, and were greater during exercise compared with young women (*P < 0.05 vs. Rest within condition). C, postjunctional α2‐adrenoceptor stimulation (via intra‐arterial clonidine) reduced vascular conductance similarly in resting skeletal muscle of young and older men during infusion of the vasodilator adenosine (filled bars). In contrast, vasoconstrictor responses during moderate intensity handgrip exercise were greater in older men relative to young men (open bars) († P < 0.05 vs. Adenosine within condition; *P < 0.05 vs. Young). The collective data demonstrate impaired modulation of sympathetic α‐adrenoceptor vasoconstriction in contracting muscle of older adults. From Koch et al. (2003), Fadel et al. (2004) and Dinenno et al. (2005).
