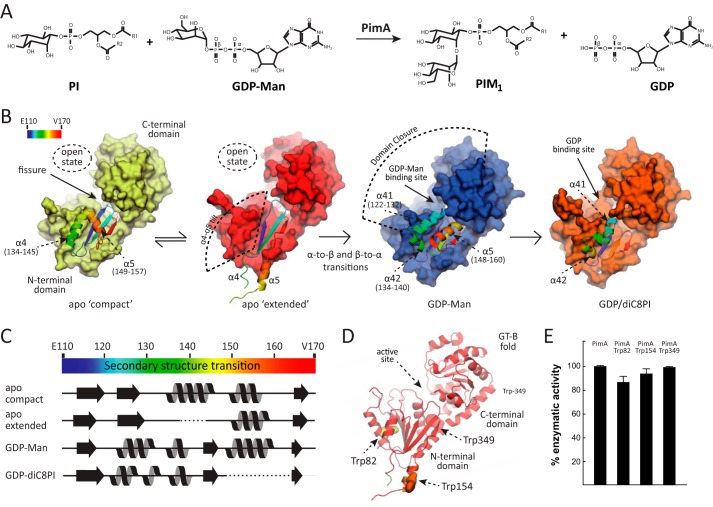
FIGURE 1.
Biosynthesis of PIMs in mycobacteria. A, PimA transfers a Manp residue from GDP-Man to the 2-position of the myo-inositol ring of PI to form phosphatidyl-myo-inositol monomannoside (PIM1). The reaction occurs with retention of the anomeric configuration of the sugar donor. B, schematic representation showing the crystal structures of PimA, including its apo compact, apo extended, PimA-GDP-Man, and PimA-GDP-diC8PI complexes (11, 12). The dynamic N-terminal region is shown in rainbow-colored schematic representation. C, secondary structure elements of a selected region corresponding to residues 110–170, as observed in the apo compact, apo extended, PimA-GDP-Man, and PimA-GDP-diC8PI complexes. D, location of Trp-82, Trp-154, and Trp-349 in the N-terminal Rossmann domain of the GT-B mannosyltransferase PimA. E, activity measurements showing that PimA-Trp-82, PimA-Trp-154, and PimA-Trp-349 mutant variants are functional proteins. The enzymatic activities of the three double mutants are shown as a percentage of the wild type activity. Data represent mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments.