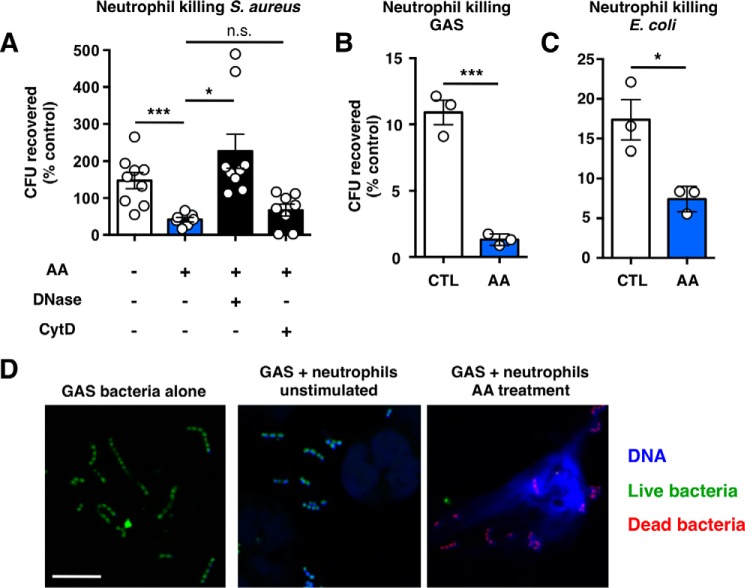
FIGURE 7.
Anacardic acid enhances bacterial killing. A, neutrophil killing of USA300 MRSA. Control represents bacteria exposed to unstimulated neutrophils and anacardic acid represents neutrophils treated with 10 μm anacardic acid. DNase (7.5 units/ml) or cytochalasin D (10 μg/ml) were added to inhibit NET- or phagocytosis-based killing, respectively (n = 9). B and C, neutrophil killing of group A Streptococcus (B) and E. coli (C) by unstimulated or anacardic acid-treated (AA; 10 μm) neutrophils; representative experiments of three independent experiments performed in triplicate are shown. D, confocal microscopy visualization of live/dead (green/red) stained group A Streptococcus in the presence of human neutrophils stimulated with anacardic acid (10 μm). The scale bar represents 10 μm. Unless otherwise noted, data shown are expressed as mean values ± S.E. and represent the results of at least three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Where applicable, the results were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance and post hoc Newman Keuls test. ***, p < 0.001 versus control values. ctrl, control.