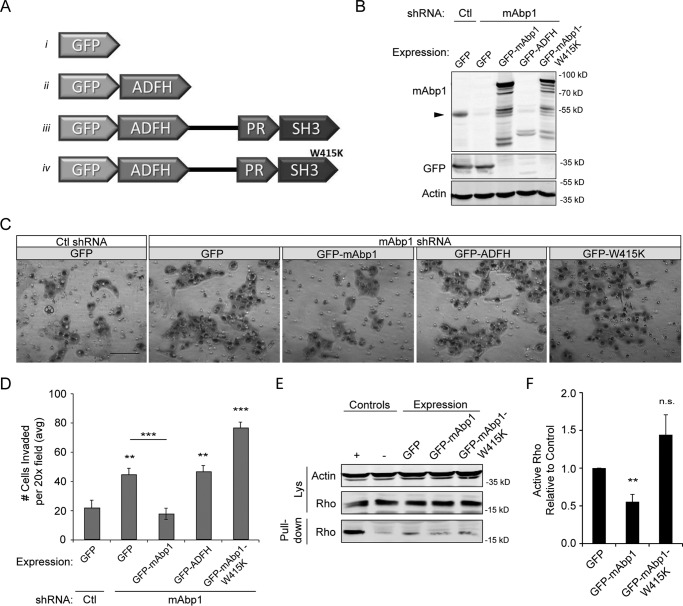
FIGURE 3.
mAbp1 regulates MTLn3 cell invasion. A, schematic of GFP constructs with the ADFH domain alone, WT mAbp1 and mAbp1-W415K (SH3 domain mutant). B, control or mAbp1 shRNA MTLn3 cells were transiently transfected with GFP constructs, and lysates were probed for mAbp1, GFP, and actin as a loading control. The Western blot was cut to immunostain GFP and mAbp1 separately; however, GFP staining of all constructs can be seen in Fig. 4D. The arrow denotes endogenous mAbp1 expression in control and mAbp1 shRNA cells. C, transiently transfected MTLn3 cells were serum-starved for 24 h, seeded in Matrigel coated boyden chambers, and allowed to invade toward serum-containing media for 16 h. Representative images of invaded cells at 20× magnification. Scale bar = 100 μm. D, quantification of invasion of transiently transfected control or mAbp1-deficient cells. Average number of cells invaded from 12 images taken at 20× magnification. n = 4. **, p = 0.0067; ***, p = 0.0010; **, p = 0.0080; ***, p = 0.0003. E, MTLn3 cells overexpressing GFP, GFP-mAbp1, or GFP-mAbp1-W415K were serum-starved then treated with 5 nm EGF for 5 min. Active Rho was pulled down with Rhotekin binding beads and probed for RhoA and actin as a loading control. Overexpression of mAbp1, but not the SH3 mutant mAbp1-W415K, reduced RhoA activity in mAbp-deficient cells. F, quantification of active RhoA pulled down by densitometry analysis. The amount of active RhoA was normalized to control; n = 3. **, p = 0.0056. ns, not significant. Error bars represent S.E.