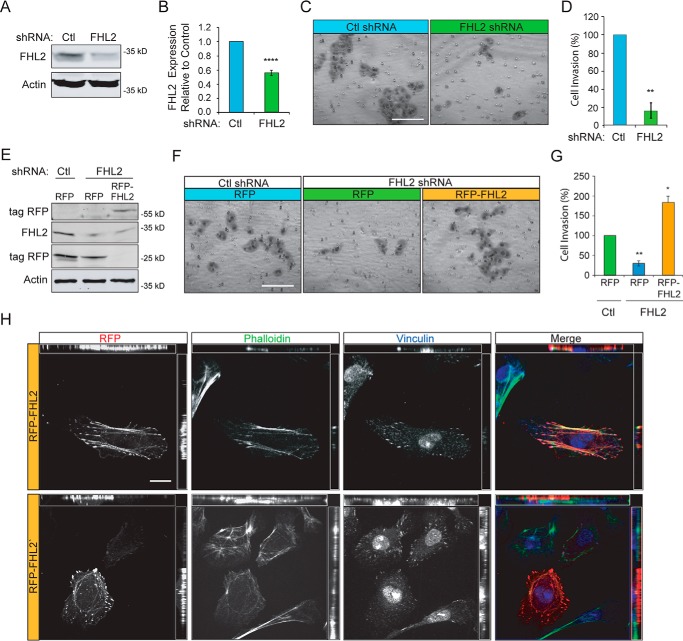
FIGURE 5.
FHL2 mediates invasive migration of MTLn3 breast cancer cells. A, control and FHL2 shRNA stable lines were generated by retroviral transduction. Immunoblots were probed for FHL2 and actin as a loading control. B, quantification of FHL2 knockdown in stable shRNA lines. n = 5; ****, p < 0.0001. C, control or FHL2 shRNA cells were serum-starved 24 h, seeded in Matrigel coated boyden chambers, and allowed to invade toward serum-containing media for 16 h. Representative images of invaded cells on a membrane at 20× magnification. Scale bar = 100 μm. D, quantification of cell invasion. Percentage of cell invasion relative to control from 12 images taken at 20× magnification and normalized to control. Data are from three independent experiments. **, p = 0.0044. E, exogenous FHL2 expression rescues invasion. RFP or RFP-FHL2 were transiently expressed in control or FHL2 shRNA MTLn3 cell lines. Lysates were probed for RFP, FHL2, and actin as a loading control. F, representative images of invasion of FHL2-deficient cells transiently expressing RFP or RFP-FHL2. Cells were serum-starved 24 h and invaded through Matrigel toward serum media for 16 h. Scale bar = 100 μm. G, percentage of cell invasion relative to control from 12 images taken at 20× magnification. Data are from three independent experiments. *, p = 0.0297; **, p = 0.0040. H, representative images of RFP-FHL2 in FHL2 shRNA cells labeled with Alexa 488 phalloidin (green) and vinculin immunostaining (blue). RFP-FHL2 localizes to focal adhesions and stress fibers and occasionally in the nucleus similar to endogenous FHL2. Scale bar = 20 μm.