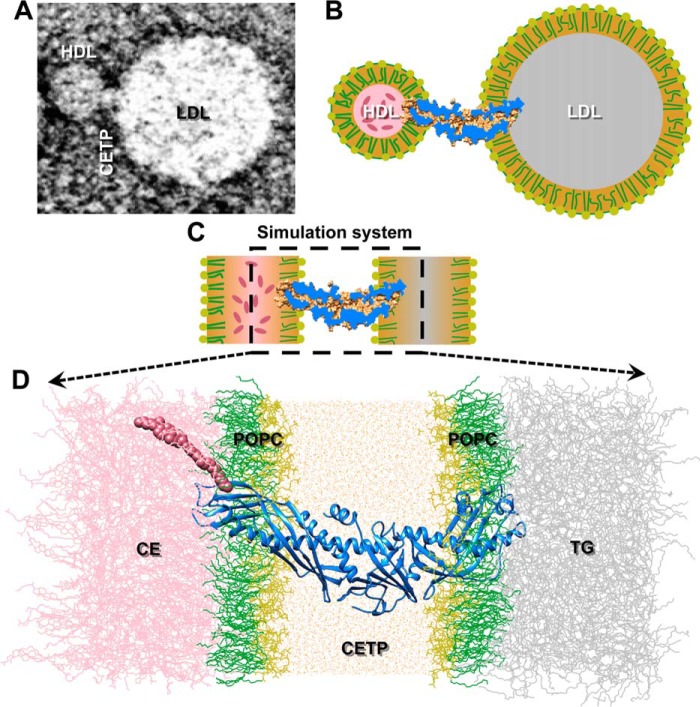
FIGURE 1.
Simulation system for studying CE transfer. A, a representative negative staining EM image shows that CETP bridged HDL and LDL, forming a ternary complex (shown in schematic in B). C, a simplified simulation system (shown in schematic) was used to simulate the ternary complex to elucidate CE transfer from HDL to LDL at an atomic level. D, the N-terminal β-barrel domain of the CETP was inserted ∼35 Å deep into a POPC monolayer adhered to a CE pool, whereas the C-terminal β-barrel domain penetrated ∼32 Å inside an opposing POPC monolayer attached to a TG pool. The region between the two opposing lipid monolayers was filled with water molecules. The POPC headgroups and fatty tails are colored yellow and green, respectively, and the CE, TG, CETP, and water molecules are colored pink, gray, blue, and orange, respectively. The CE molecule is highlighted using van der Waals spheres.