FIGURE 4.
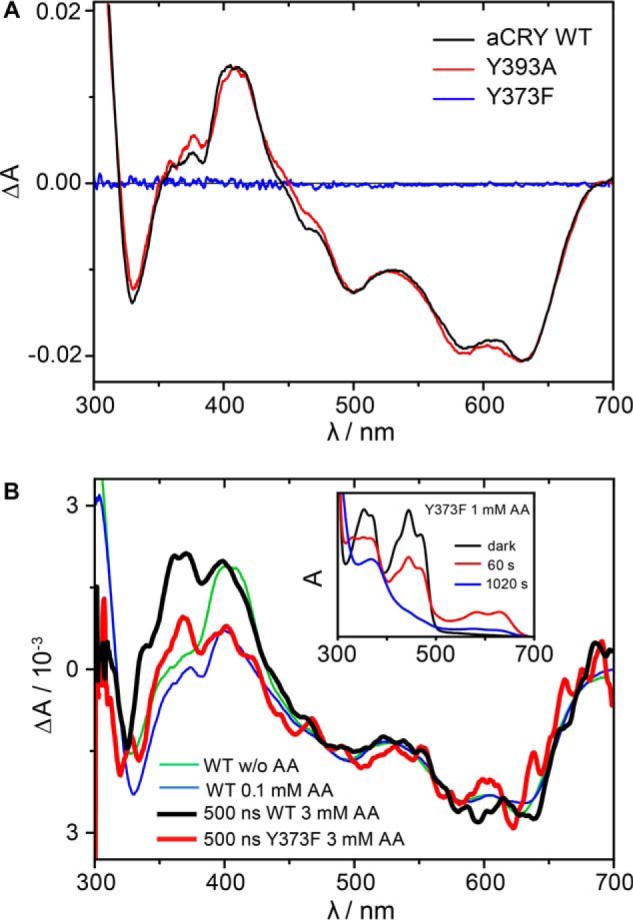
Effects of mutations in tyrosine residues on the red-light response of aCRY. A, red light-induced UV-vis difference spectra of the wild type, the Y393A and Y373F mutants of aCRY. Pre-illuminated samples were illuminated for 10 s with 632 nm. In both the wild type and the Y393A mutant, FADH• is converted to FADH− accompanied by the formation of TyrO•. The Y373F mutant does not show any light response. B, time-resolved absorption spectra at 500 ns of the Y373F mutant and wild type aCRY in the presence of 3 mm ascorbic acid. Both the Y373F mutant and the wild type show the conversion of FADH• to FADH−. In contrast to the wild type, the Y373F mutant does not show an additional contribution of TyrO• at 416 nm identifying Tyr-373 as the origin of this absorption. The conversion of FADox to FADH• and FADH− is observed in aCRY-Y373F only in the presence of ascorbic acid (inset).
