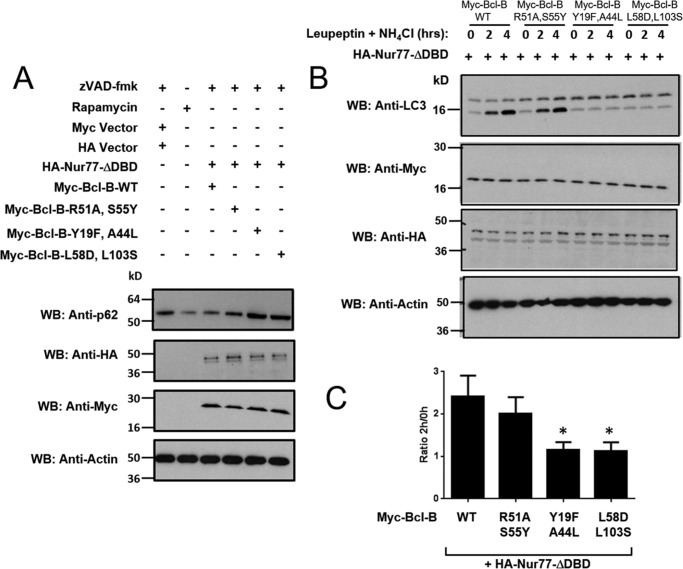
FIGURE 9.
The Nur77 binding site on Bcl-B modulates the autophagy phenotype. A, the levels of p62 were assessed in H4 cells treated with the autophagy inducer rapamycin (25 μg/ml) for 16 h (second lane) or in H4 cells in which Myc-tagged-Bcl-B WT or mutants were co-expressed with HA-tagged Nur77ΔDBD in the presence of 15 μm Z-VAD-fmk for 24 h (third to sixth lanes). An equal amount of protein from each cell lysate was analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-p62, anti-HA, and anti-Myc antibodies. Actin served as a loading control. WB, Western blotting. B, H4 cells were co-transfected with various Myc-tagged Bcl-B plasmids (WT and the R51A/S55Y, Y19F/A44L, and L58D/L103S double mutants) with HA-Nur77ΔDBD for 24 h. Cells were then treated with the lysosomal inhibitors leupeptin (100 μm) and NH4Cl (20 mm) for 2 or 4 h. The levels of LC3-I and LC3-II were analyzed by immunoblotting of total cell lysates with anti-LC3 antibody in addition to anti-myc, anti-HA, and anti-actin to verify equal protein expression and loading. C, the LC3-II bands in B were quantified using scanning densitometry. The levels of LC3-II after 2 h of leupeptin and NH4Cl treatment were divided by the level of LC3-II without lysosomal inhibitor treatment to calculate LC3 flux (mean ± S.E., n = 5). *, p < 0.05 in comparison with Bcl-B-WT + Nur77.