FIGURE 1.
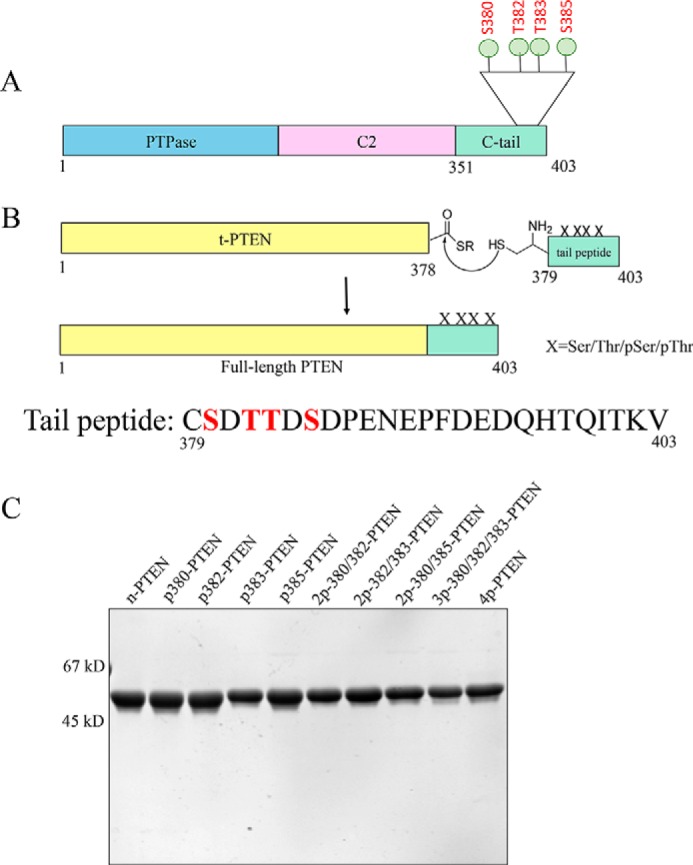
Generation of unmodified, mono-, di-, tri-, and tetraphosphorylated semisynthetic PTEN proteins. A, PTEN is composed of a protein-tyrosine phosphatase (PTPase) domain, a C2 domain, and a regulatory C-terminal tail. The cluster of phosphorylation (Ser380, Thr382, Thr383, and Ser385) is highlighted. B, C-terminal t-PTEN (amino acids 1–378) with a thioester at the C terminus is generated from intein fusion, treated with MESNA, and then ligated to the synthetic peptide containing different combinations of Ser(P) and Thr(P) (mono: p380, p382, p383, and p385; di: 2p-380/382, 2p-380/385, and 2p-382/383; tri: 3p-380/382/383; and tetra: 4p-380/382/383/385). X, Ser/Thr/Ser(P)/Thr(P). C, Coomassie-stained 10% SDS-PAGE gel of the set of differentially phosphorylated semisynthetic PTEN proteins. Ligation of t-PTEN-thioester and the specific peptide proceeds at a constant rate for 48 h, and the full-length PTEN is further purified by FPLC-anion exchange chromatography using MonoQ column. The final protein is >90% pure. First lane, n-PTEN; second lane, p380-PTEN; third lane, p382-PTEN; fourth lane, p383-PTEN; fifth lane, p385-PTEN; sixth lane, 2p-380/382-PTEN; seventh lane, 2p-382/383-PTEN; eighth lane, 2p-380/385-PTEN; ninth lane, 3p-380/382/383-PTEN; tenth lane, 4p-PTEN.
