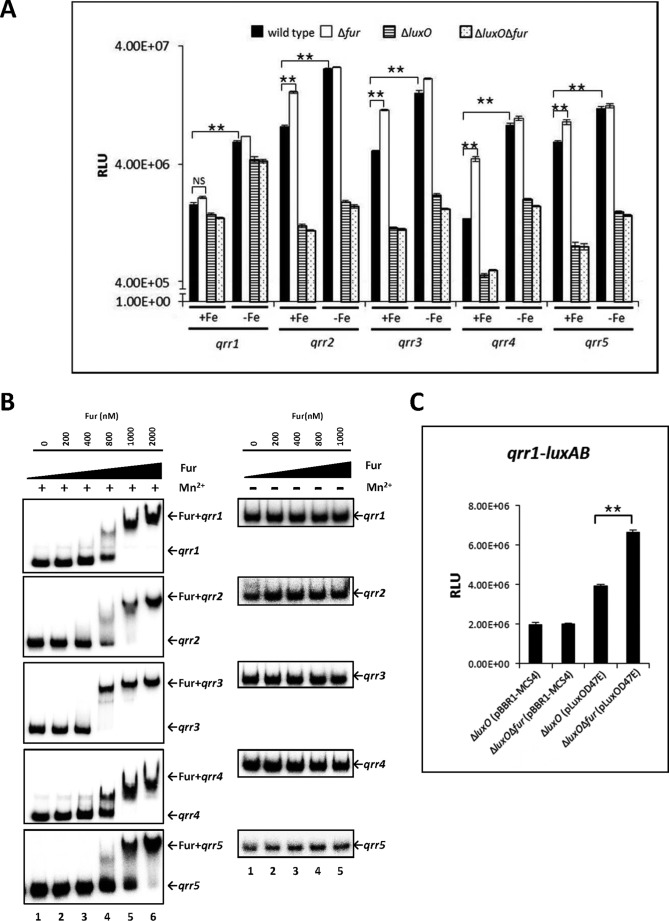
FIGURE 5.
qrr transcription regulated by iron in V. vulnificus. A, regulation of qrr transcription by iron and Fur. Luciferase activity represents levels of luxAB-transcriptional reporter fusions to qrr1, qrr2, qrr3, qrr4, and qrr5 in wild type V. vulnificus, Δfur, ΔluxO, and ΔfurΔluxO harboring each of the plasmids pHK-qrr1, pHK-qrr2, pHK-qrr3, pHK-qrr4, and pHK-qrr5. Bacteria were cultured with or without 200 μm of the iron chelator 2,2′-dipyridyl, which was supplemented when cells were at an A600 of ∼0.2. Cell density and luminescence were measured at log phase (A600 of ∼0.6), as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Relative light units (RLU) represent light units normalized to cell density (luminescence/A600). Values are averages from three biological experiments, and error bars denote standard deviations. B, binding of Fur to the promoter regions of qrr genes as determined by electrophoresis mobility shift assay. Ten ng of DNA probes, including qrr promoter regions, were incubated with increasing concentrations of Fur in the presence (left panel) or absence (right panel) of 100 μm MnSO4. Lanes 1–6 represent Fur concentrations of 0, 200, 400, and 800 nm and 1 and 2 μm, respectively. C, Fur significantly represses transcription of qrr1 in the presence of overexpressed luxOD47E. ΔluxO and ΔfurΔluxO harboring pHK-qrr1 and pLuxOD47E or pBBR1-MCS4 were cultured until log phase. Values are averages from three independent experiments, and error bars denote standard deviations (A600 of ∼0.6). Expression of qrr1 was measured as described above (**, p < 0.005; NS, not significant in Student's t test with p > 0.05).