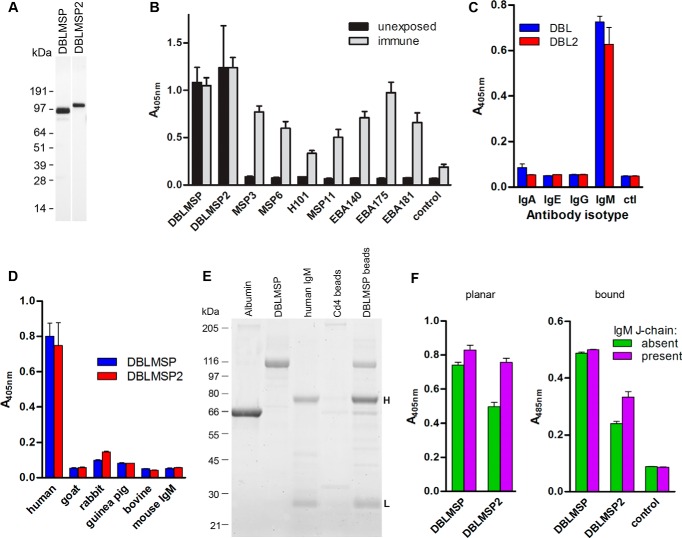
FIGURE 1.
Recombinant P. falciparum DBLMSP and DBLMSP2 bind human IgM. A, anti-biotin Western blot showing expression of recombinant monobiotinylated DBLMSP and DBLMSP2 proteins from mammalian cells. B, DBLMSP and DBLMSP2 are immunoreactive with control, naïve human sera. Enzymatically monobiotinylated recombinant parasite proteins were immobilized on streptavidin-coated plates, and their immunoreactivity to pooled sera from either unexposed individuals (black bars) or immune Kenyan adults (gray bars) was tested. C, DBLMSP (blue) and DBLMSP2 (red) bind purified human IgM and no other immunoglobulin isotype, relative to no immunoglobulin control (ctl). D, DBLMSP and DBLMSP2 binding was restricted to human IgM, and did not bind sera from other species, including purified murine IgM. E, streptavidin-coated paramagnetic beads were coated in monobiotinylated His6-tagged recombinant DBLMSP or a control protein (Cd4-d3 + 4) and incubated in the presence of normal human serum. Following elution and resolution by SDS-PAGE, 80- and 25-kDa bands corresponding to the heavy (H) and light (L) chains of human IgM, respectively, were observed in the DBLMSP but not the negative control pulldown. Purified albumin, DBLMSP, and IgM protein are shown for comparison on the left. F, both DBLMSP and DBLMSP2 bound chimeric IgM containing human heavy chains regardless of whether it was antigen-bound (right panel) or not (left panel). Both DBLMSP and DBLMSP2 could bind IgM that contained or lacked a J-chain, although DBLMSP2 binding to IgM lacking a J-chain was reproducibly weaker. Negative control was the Cd4 tag alone. B–D and F represent one representative from two or more ELISA experiments; bars represent means ± S.D.; n = 3 replicate wells.