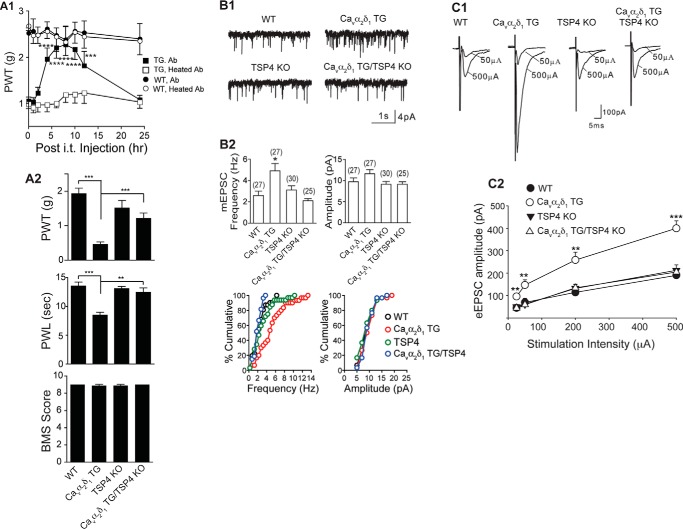
FIGURE 3.
Depleting or blocking TSP4 reverses Cavα2δ1-induced pain states and dorsal horn neuron sensitization. A1, TSP4 antibody (Ab, chicken, 10 μg/5 μl/mouse, i.t.), but not heated TSP4 antibody, reversed allodynia induced by neuronal Cavα2δ1 overexpression in the Cavα2δ1-TG mice without affecting baseline sensitivity in WT mice. Data are the means ± S.E. from n = 5 (WT) or 6 (TG). ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001 versus pretreatment level by repeated measures two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests. A2, TSP4 ablation did not affect baseline sensitivity but reversed tactile allodynia (top) and thermal hyperalgesia (middle) in the Cavα2δ1 TG mice. Locomotor functions were not affected in these genetically modified mice as analyzed with the Basso Mouse Scale for locomotion (BMS), bottom). Data are the means ± S.E. from n = 8–10 each group. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 by Student's t test. B1, mEPSCs from L4 superficial dorsal horn neurons of the same mouse groups. Cavα2δ1-induced increase of mEPSC frequency in the Cavα2δ1 TG mice was blocked by TSP4 ablation. B2 top, summarized data. Data are the means ± S.E. from the number of neurons shown in parentheses that were obtained from ≥ 5 mice in each group. *, p < 0.05 versus WT by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests. B2 bottom, cumulative distribution of mEPSC frequency and amplitude in each group (p < 0.01 for frequency comparisons between the Cavα2δ1 TG group and each of the other three groups; Kolmogorov-Smirnov test). C1, TSP4 ablation also blocked Cavα2δ1-induced increase of eEPSC amplitude in response to dorsal root entry zone stimulation without affecting baseline eEPSCs significantly. C2, summarized data, means ± S.E. from n ≥ 7 for each stimulus intensity (≥5 mice). **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 versus WT by repeated measures two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests.