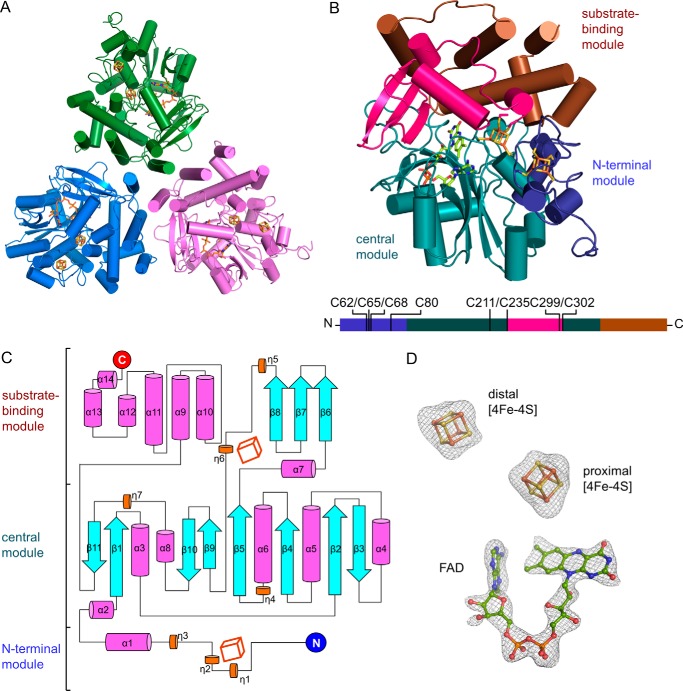
FIGURE 3.
Structure of HCAR. A, HCAR trimer in trefoil shape. Protomers are colored in green, blue, and purple, respectively. B, structure of an HCAR protomer. Three functional modules are color-indicated. The [4Fe-4S] clusters with their ligating cysteines and the redox cofactor FAD are shown as sticks. An overview of the functional modules of HCAR is shown at the bottom with the ligating cysteines indicated. The overall structure is divided into three functional modules, which are the N-terminal module (residues 27–100), the central module (101–235, 303–358), and the substrate-binding module (236–302, 359–462). C, topology of the secondary structure elements of HCAR. The N and C termini are indicated as blue and red circles. α-Helix and 310 helix are shown as magenta and orange cylinders, and β-strands are shown as cyan arrows. Two [4Fe-4S] clusters are shown as cubes. D, defined electron density of the cofactors. The |Fo| − |Fc| omit map is contoured at 3σ as gray mesh.