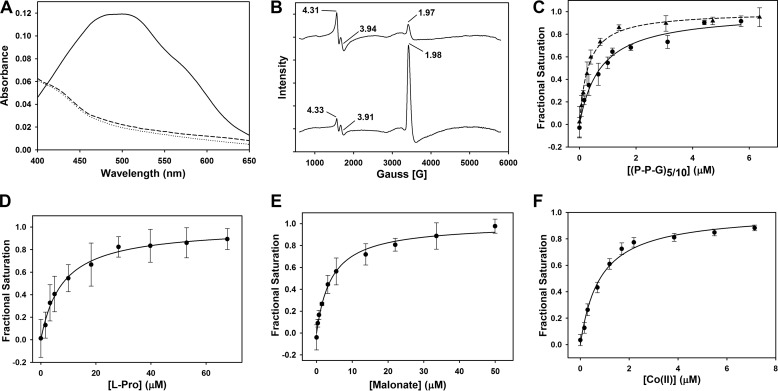
FIGURE 2.
Spectral properties and substrate/cofactor binding affinities (Kd) of Fe(II)-BaP4H. A, UV-visible spectra of the reaction of 776 μm apo-BaP4H in the presence of Fe(II) and αKG. Apo-BaP4H, dotted line; Fe(II)-BaP4H, dashed line; Fe(II)-BaP4H-αKG ternary complex, solid line. B, EPR spectra of BaP4H in the presence of NO: top, 100 μm apo-BaP4H with equimolar concentration of Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2; bottom, NO-Fe(II)-BaP4H with 100 μm αKG. C, the intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence was monitored as corresponding peptides were titrated into an anaerobic solution containing 1 μm apo-BaP4H, 3 μm Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2, and 100 μm αKG. The binding affinities for the (P-P-G)10 and (P-P-G)5 peptides were determined to be 0.74 ± 0.11 μm (circles and solid line) and 0.3 ± 0.02 μm (triangles and dashed line), respectively. D, the Kd for l-proline was determined to be 7.9 ± 2.5 μm and was titrated into an anaerobic solution containing 1 μm BaP4H, 3 μm Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2, and 100 μm αKG. E, the Kd (4.2 ± 0.5 μm) for malonate was obtained by titrating it into an anaerobic solution containing 1 μm BaP4H and 3 μm Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2. F, the Kd for Co(II) was determined to be 0.81 ± 0.09 μm. CoCl2 was titrated into an aerobic solution containing 1 μm BaP4H.