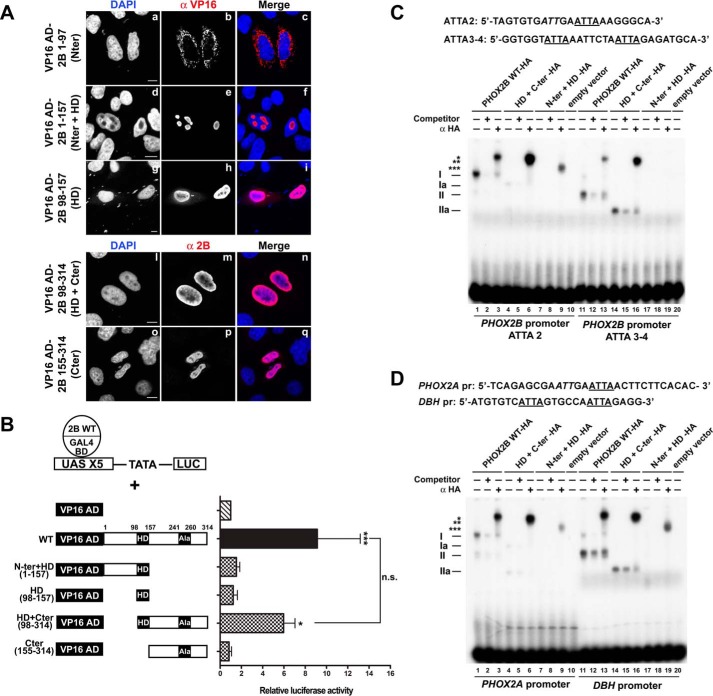
FIGURE 7.
Mapping of the PHOX2B dimerization domain and contribution of the N- and C-terminal domains to dimerization and DNA binding of PHOX2B. A, representative immunofluorescence images of the localization of the VP16 AD-PHOX2B deleted fusion proteins (VP16 AD-Nter, VP16 AD-Nter + HD, VP16 AD-HD, VP16 AD-HD + Cter, VP16 AD-Cter) in transfected HeLa cells stained using anti-VP16 (b, e, and h) or anti-PHOX2B antibody (m and p). The nuclei were visualized using DAPI (a, d, g, l, and o) and merged with the proteins detected by the anti-VP16 and anti-PHOX2B antibodies (c, f, i, n, and q). Scale bars, 10 μm. B, luciferase assays. The bars indicate the transcriptional activity of the pG5LUC reporter construct in HeLa cells upon co-transfection with a vector containing the cDNA of wild-type protein fused to GAL4 BD (GAL4 BD-PHOX2B WT) in combination with the empty vector containing VP16 AD (hatched bar), VP16 wild-type fusion protein (black bar), or VP16-PHOX2B deleted fusion protein shown on the left (cross-hatched bars). The results are the mean values ± S.D. (error bars) of the transcriptional activity of the constructs detected in at least three experiments performed in triplicate (n = 4) and are expressed as -fold increases over the activity of the reporter plasmid co-transfected with the GAL4 BD-PHOX2B WT protein (= 1; hatched bar). *, significant differences from the activity of the wild-type protein fused to GAL4 BD (ANOVA, Tukey's test, p < 0.05); ***, significant differences from the activity of the wild-type protein fused to GAL4 BD (ANOVA, Tukey's test, p < 0.001); n.s., not significant (ANOVA, Tukey's test). C and D, gel shift assays using oligonucleotide probes corresponding to two regions of the PHOX2B promoter (C) or a region of the PHOX2A and DBH promoters (D) containing the ATTA core motifs known to bind PHOX2B. At the top, the sequences of the oligonucleotides used as probes; the ATTA core motif is underlined, and the incomplete motif is in italic type. The labeled probes were incubated with in vitro expressed HA-tagged PHOX2B wild-type protein (lanes 1–3 and 11–13), PHOX2B HD + Cter (lanes 4–6 and 14–16), or PHOX2B Nter + HD proteins (lanes 7–9 and 17–19). The in vitro translated pcDNA3 empty vector was used as a control to exclude nonspecific interactions (lanes 10 and 20). The competitions were carried out by adding a molar excess of unlabeled oligonucleotide (lanes 2, 5, 8, 12, 15, and 18). Supershift experiments were performed by preincubating the in vitro expressed proteins with anti-HA antibody (lanes 3, 6, 9, 13, 16, and 19). The Roman numerals on the left indicate the specific retarded complexes obtained using in vitro expressed PHOX2B wild-type protein (I and II) or PHOX2B HD + Cter (Ia and IIa); the asterisks indicate the supershifted complexes containing PHOX2B. The free probes are shown at the bottom of the gels.