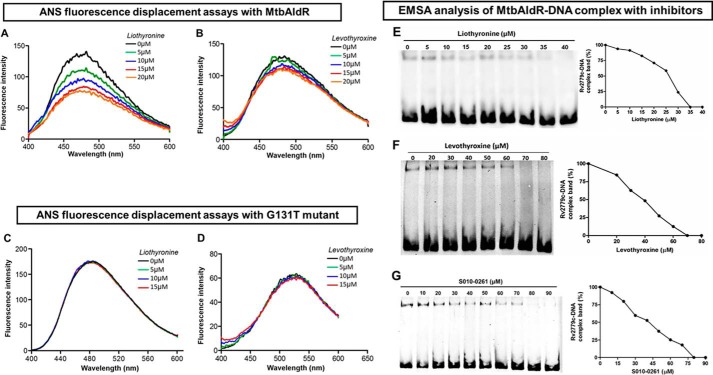
FIGURE 6.
Inhibitor/ligand binding studies using ANS fluorescence displacement assays against MtbAldR and its G131T mutant. A and B correspond to the experiments with liothyronine and levothyroxine with MtbAldR, whereas C and D correspond to the experiments involving the inactive G131T mutant. Clearly, liothyronine and levothyroxine exhibit binding to the native protein, but they are unable to bind to the G131T mutant. The y axis represents the fluorescence intensity in arbitrary units, and the x axis corresponds to the scanned wavelength. In the experiments, the MtbAldR-ANS premix or the G131T-ANS premix, was titrated against increasing concentration of the respective compounds, and the resultant change in the fluorescence intensity was monitored. The concentrations of the compound used in each curve are shown as insets in the respective panels. Subsequently, the ability of liothyronine (E), levothyroxine (F), and a tetrahydroquinoline carbonitrile derivative (S010-0261) (G) to inhibit the MtbAldR-DNA complex was probed using EMSA. The first lane in the panels corresponds to the control experiments containing only protein and no compound. The subsequent lanes correspond to increasing concentrations of the added compounds. The IC50 values of liothyronine, levothyroxine, and S010-0261 were found to be ∼25, 40, and 42 μm.