FIGURE 8.
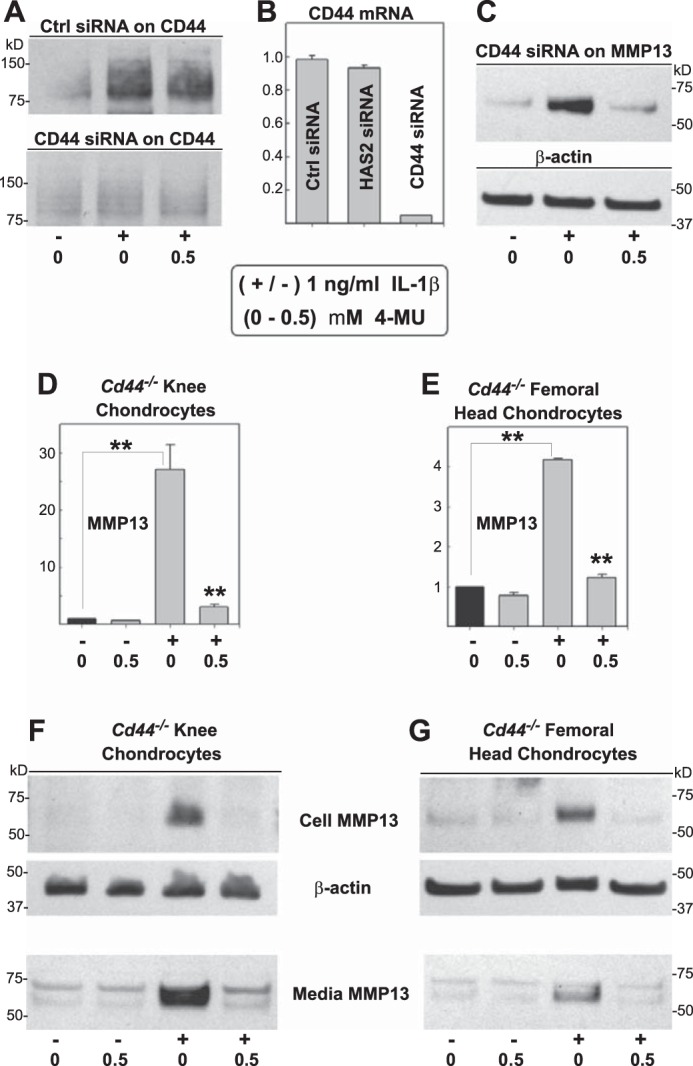
Modulation of CD44 and the effect on 4-MU inhibition of IL-1β. To determine whether CD44 was required for cells to detect changes in extracellular HA, such as changes in HA that occur due to 4-MU, CD44 depletion experiments were performed. In a first approach, human chondrocytes were transfected with control, HAS2-specific or CD44-specific siRNA, 24 h before the addition of 1.0 ng/ml IL-1β and 0 or 0.5 mm 4-MU for 24 h as indicated. A depicts the effects of siRNA treatment on CD44 protein as detected by Western blot analysis; B depicts the effects on siRNA on CD44 mRNA levels; and C depicts the effects of Cd44 siRNA on MMP13 protein in the medium of cells treated without or with IL-1β and 4-MU. In a second approach, murine chondrocytes derived from Cd44−/− knee condylar (D and F) or femoral head (E and G) cartilage were incubated without or with 1.0 ng/ml IL-1β and 0.5 mm 4-MU for 24 h. In some experiments, cell lysates were prepared for real time qRT-PCR, wherein the fold change (y axes) in mRNA copy number for MMP13 was compared with control conditions and quantified using the ΔΔCt approach with normalization to GAPDH (D and E). In other experiments, cell lysates and media fractions were processed for Western blotting for MMP13 and β-actin protein (F and G). For statistical analysis, a two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer test was used; **, p < 0.01.
