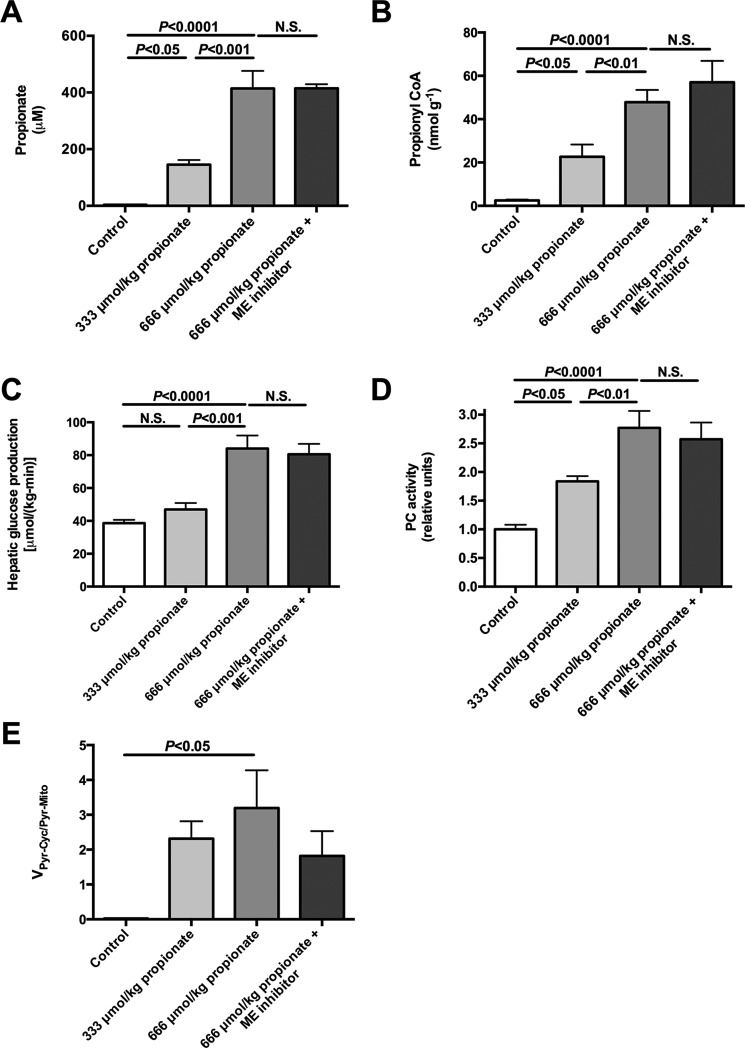
FIGURE 4.
Continuous intra-arterial propionate infusion (low dose = 333 μmol/kg = 2. 8 μmol/(kg-min) × 120 min; high dose = 667 μmol/kg = 5.6 μmol/[kg-min × 120 min) markedly increases plasma propionate concentrations, hepatic propionyl-CoA concentrations, hepatic glucose production rates, and stimulates PC activity as well as VPK + ME/VPC + PDH flux in a dose-dependent manner. A, plasma propionate concentrations. B, liver propionyl-CoA concentrations. C, hepatic glucose production. D, ex vivo PC activity. E, VPK + ME/VPC + PDH flux. Data are mean ± S.E. of n = 6 per group. N.S., not significant.