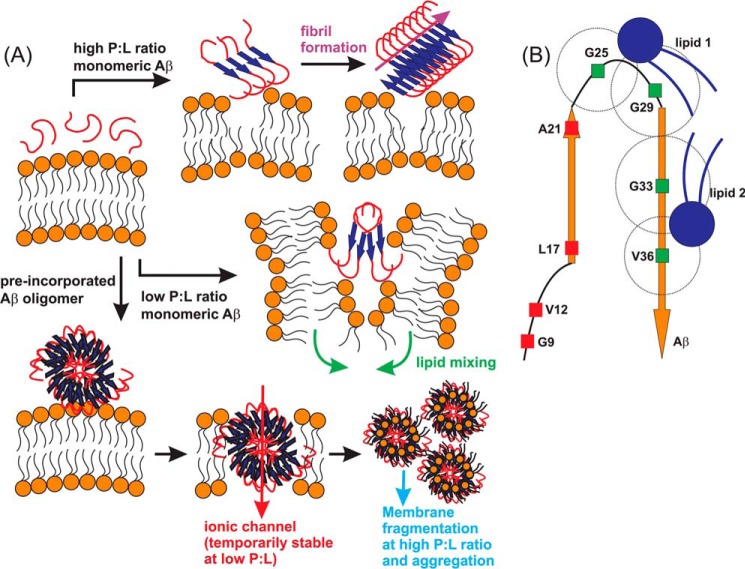
FIGURE 7.
A, proposed membrane interaction pathways under different conditions of initial Aβ oligomeric states and P:L molar ratio. Fibrillation and vesicle fusion are induced by membrane interactions of monomeric or small oligomeric Aβ peptides. Membrane fragmentation and Aβ-lipid aggregates are induced by membrane interactions of preformed large Aβ oligomers, with the possibility of forming ionic channels. B, schematic of binding between Aβ and lipids in the Aβ-lipid aggregates based on solid-state NMR measurements. A possible binding model between Aβ and phospholipids, derived from solid-state NMR 13C,31P REDOR experiments. The best fit distances for four specific residues, Gly-25, Gly-29, Gly-33, and Val-36, are shown with dashed circles, which indicate the possible binding sites of phospholipids. At least two binding sites are required to fulfill the experimental results. The schematic is drawn in scale.