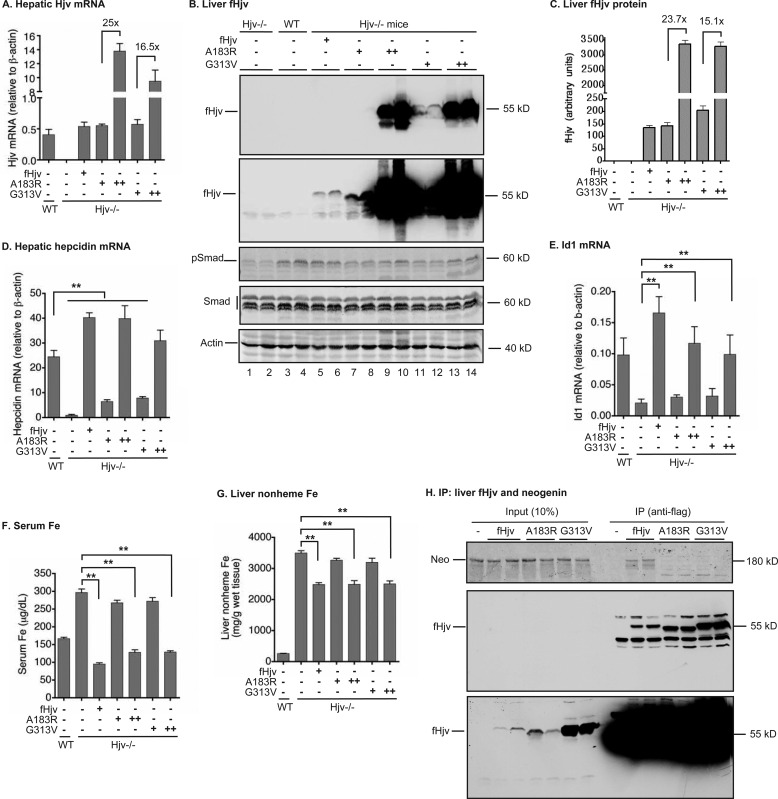
FIGURE 2.
Both A183R and G313V-fHjv had a reduced ability to induce the BMP signaling and hepcidin expression in Hjv−/− mice. Eight-week-old male Hjv−/− mice were intraperitoneally injected with AAV8-fHjv, A183R-fHjv, or G313V-fHjv at ∼5 × 1011 (+) and/or ∼1013 (++) genome-particles per mouse. Age and gender-matched WT and Hjv−/− mice were included as controls. A, qRT-PCR analysis of Hjv mRNA in the liver. B, Western blot analysis of fHjv, pSmad1/5/8 (pSmad), total Smad1/5/8 (Smad), and β-actin in 150 μg of liver extracts from two mice for each condition. C, quantification of fHjv bands in the Western blot images of liver extracts by Licor. D and E, qRT-PCR analysis of hepcidin and Id1 mRNA in the liver. F, serum iron analysis. G, liver nonheme iron analysis. H, co-immunoprecipitation of fHjv with neogenin in the liver. About 3 mg of liver extract protein from Hjv−/− mice injected with AAV8-fHjv, A183R-fHjv, and G313V-fHjv vectors at ∼5 × 1011 genome particles per mouse was immunoprecipitated by using anti-FLAG M2 beads for fHjv, and immunodetected for fHjv and neogenin by using HRP-coupled mouse anti-FLAG M2 IgG and rabbit anti-neogenin FNIII 1–6 antibody, respectively. About 250 μg of extract protein for each sample was loaded as input. For all qRT-PCR analysis, the results are expressed as the amount relative to that of β-actin for each sample. The mean ± S.D. are presented. n = 5 for each group. **, p < 0.01.