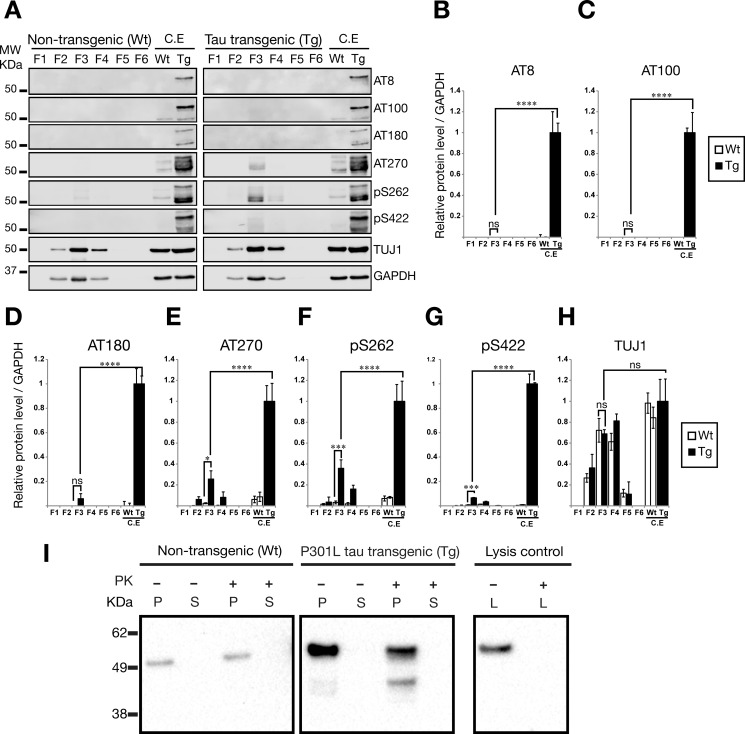
FIGURE 3.
Phosphorylation-dependent tau epitopes are present at very low levels in exosome-like EVs isolated from mouse brains. Shown are Western blotting analysis of sucrose fractions F1-F6, testing different AD-associated phospho-tau epitopes. 20 μg of total protein was loaded for F3 exosome-like EVs and whole cell lysate controls. Error bars represent S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001; ns, not significant. A, representative Western blots for paired helical filament-tau phospho-epitopes and additional proteins. MW, molecular weight; C.E, cell extract. B–G, quantification of protein levels for (B) AT8, (C) AT100, (D) AT180, (E) AT270, (F) Ser(P)-262, and (G) Ser(P)-422. Analysis reveals that F3, enriched for exosome markers, contains the phospho-tau epitopes AT270, Ser(P)-262, and Ser(P)-422. Interestingly, the AT8, AT100, and AT180 phospho-epitopes are not detected in exosome-like EVs. H, protein levels for neuron-specific class III β-tubulin (TUJ1), demonstrating the neuronal origin of the EVs. I, PK surface shaving was performed with exosome-like EVs in sucrose fraction F3 (0.95 m sucrose). Total tau was assayed with the Tau5 antibody. No tau was identified in the supernatant (S) after PK treatment. Tau was associated with the pellet (P) of intact exosome-like EVs after centrifugation in both WT and Tg mice. Tau protein was completely degraded when PK was added to lysed EVs (L).