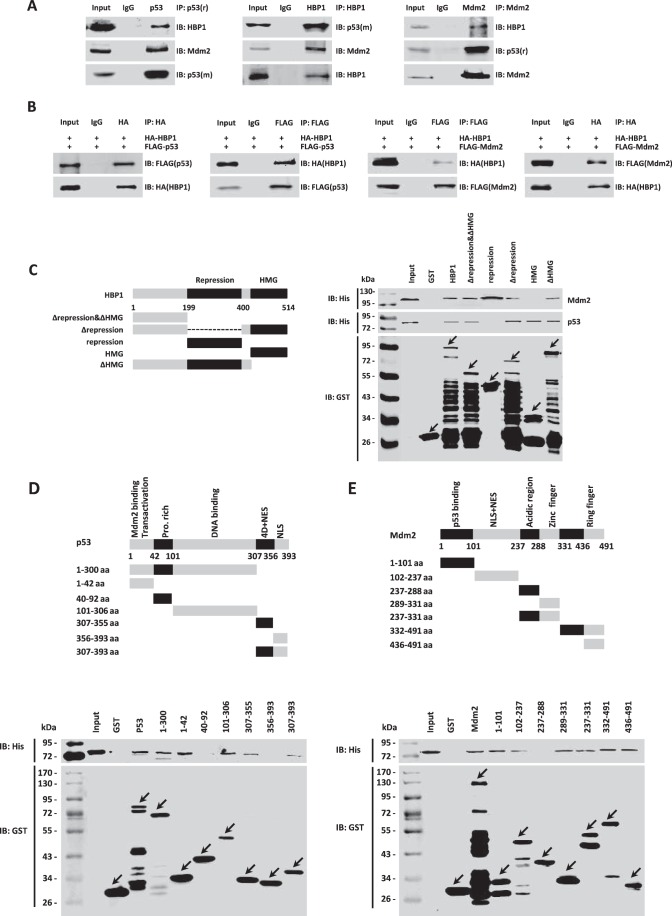
FIGURE 3.
HBP1 interacts with both p53 and Mdm2 in vivo and in vitro. A and B, HBP1 interacts with both p53 and Mdm2 in vivo. A549 cells were lysed with IP lysis buffer and then subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-p53 (9282), HBP1, or Mdm2 antibodies followed by Western blotting analysis (A). H1299 cells were cotransfected with HA-HBP1 and FLAG-p53 or FLAG-Mdm2. The IP assay was carried out by using anti-HA/FLAG antibody and followed by Western blotting with anti-FLAG/HA antibody. The same samples were immunoblotted (IB) against HA/FLAG to determine immunoprecipitation efficiency (B). C–E, HBP1 interacts with both p53 and Mdm2 in vitro. Shown is a schematic of N-terminal GST-tagged, full-length HBP1 along with its various deletion mutants (C, left panel), p53 along with its various deletion mutants (D, top panel), and Mdm2 along with its various deletion mutants (E, top panel). A GST pulldown assay was carried out to determine the domain of HBP1 essential for its interaction with p53 and Mdm2 (C, right panel), the domain of p53 essential for its interaction with HBP1 (D, bottom panel), and the domain of Mdm2 essential for its interaction with HBP1 (E, bottom panel). GST pulldown efficiency was evaluated by Western blotting with anti-GST antibody.