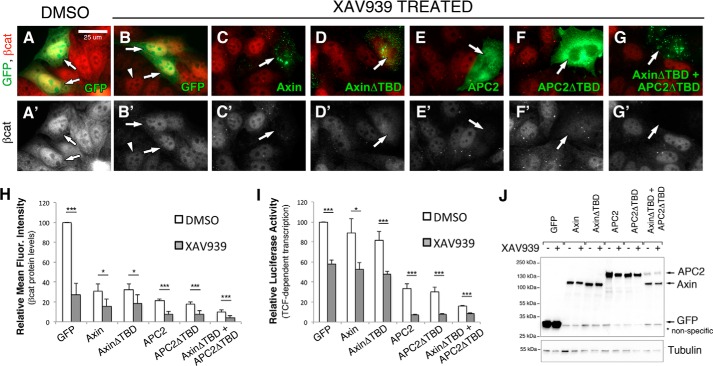
FIGURE 5.
TNKS inhibition antagonizes destruction complex activity through an additional mechanism(s) other than Axin stabilization. A–G, SW480 cells were transiently transfected with GFP-tagged APC2 or Axin proteins, treated with DMSO (A) or the TNKS inhibitor XAV939 (B–G) for 24 h, and processed for immunofluorescence. Arrows indicate transfected cells, and arrowheads point to residual nuclear βcat staining after XAV939 treatment. H, relative mean fluorescence intensity of βcat protein levels in transfected SW480 cells treated with either XAV939 or DMSO as a control. Four independent experiments were conducted, normalized to GFP DMSO, and averaged. I, TOPFlash reporter assay to determine βcat-stimulated transcriptional output in transfected SW480 cells treated with XAV939 or DMSO as a control. XAV939 treatment further reduced βcat protein levels and transcriptional output in cells transfected with Axin, AxinΔTBD, APC2, and APC2ΔTBD (all p < 0.05). Six independent experiments were conducted, normalized to GFP DMSO, and averaged. J, representative immunoblot of transfected cells from panel H. Scale bar, 25 μm. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.