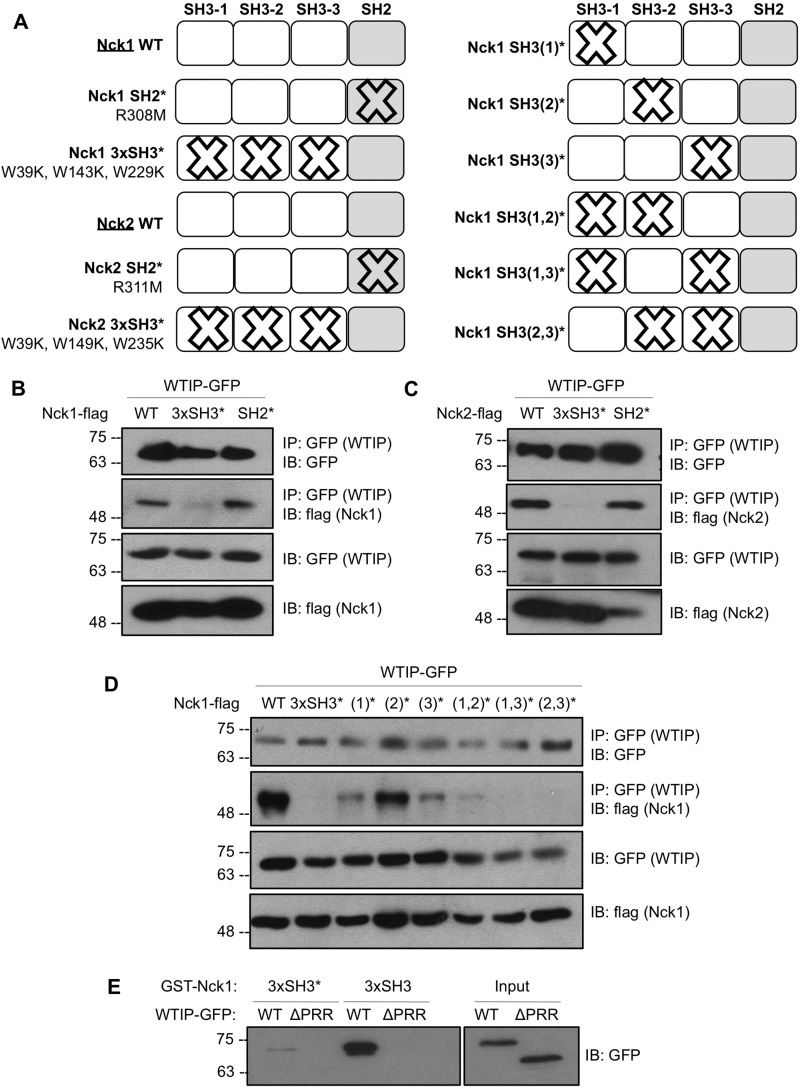
FIGURE 2.
Nck and WTIP interact via Nck SH3 domains and the WTIP PRR. A, schematic of Nck1 and Nck2 variants used in binding assays to map the interaction between Nck and WTIP, depicting point mutations and nomenclature used for inactivation of SH2 and single or multiple SH3 domains. B and C, lysates from HEK293T transiently co-expressing WTIP-GFP with Nck1-FLAG or Nck2-FLAG WT and variants with inactivated SH2 or SH3 domains were immunoprecipitated (IP) for GFP and immunoblotted (IB) for GFP and FLAG. The interaction between Nck1/2 and WTIP was abolished by inactivation of all three SH3 domains. D, lysates from HEK293T transiently co-expressing WTIP-GFP with Nck1-FLAG WT and variants with single, double-, or triple-inactivated SH3 domains were immunoprecipitated for GFP and immunoblotted for GFP and FLAG. The interaction between Nck1 and WTIP is most substantially reduced by inactivation of the first and third Nck1 SH3 domains. E, lysates from HEK293T cells overexpressing WTIP-GFP or the deletion variant WTIPΔPRR-GFP (Input) were incubated with immobilized GST fusion proteins corresponding to the three WT Nck1 SH3 domains (3xSH3) or three inactivated Nck1 SH3 domains (3xSH3*). Pulldown complexes were immunoblotted for GFP, demonstrating loss of binding between Nck1 SH3 domains and WTIPΔPRR and between Nck1 3xSH3* and full-length WTIP.