FIGURE 8.
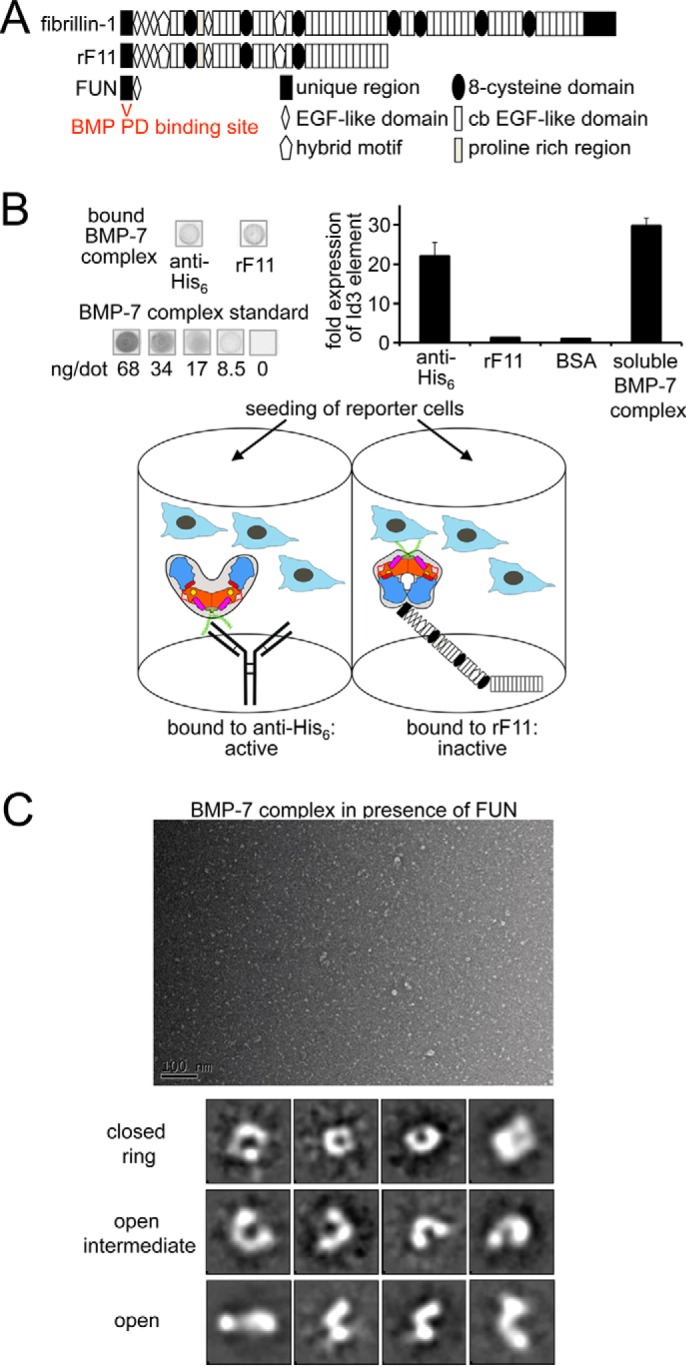
Binding to fibrillin-1 induces a conformational change of the BMP-7 complex, resulting in GF inhibition. A, domain structure of fibrillin-1 and used variants. B, BMP activity assay with BMP-7 complex captured via PD interactions, mAb against the N-terminal His6 tag, or the N-terminal half of fibrillin-1 (rF11). C2C12 cells were seeded onto immobilized BMP-7 complex, and Id3 expression was measured as a read-out for BMP activity. Shown is dot blotting analysis of stripped BMP-7 complex by comparison with a diluted series of dots containing BMP-7 complex at known concentrations. The schematic depicts the different ways BMP-7 PD-GF complex is presented to the reporter cells. Antibody capture of the N-terminally placed His6 tag on the PD (green) does not affect bioactivity; however, binding of fibrillin-1 within the PD (blue) induces a conformational change into a ring shape that confers latency. Orange, GF dimer; yellow circle, type II receptor binding site; green, N-terminal His6 tag; magenta, α1-helix; red, α2-helix; red, stretch connecting α1- and α2-helix containing the 65PHRP68 motif; light blue, C-terminal portion of BMP-7 PD. C, dialyzing the small fibrillin-1 N-terminal fragment FUN to BMP-7 complex resulted in the formation of ring shapes and open intermediates that were absent in the BMP-7 complex-only sample (Fig. 2A). Shown are a representative TEM electron micrograph (scale bar, 100 nm) and 12 from 100 class averages of 11,000 particles (box size, 28 × 28 nm). The small fibrillin-1 fragment FUN was not distinguishable from the background.
