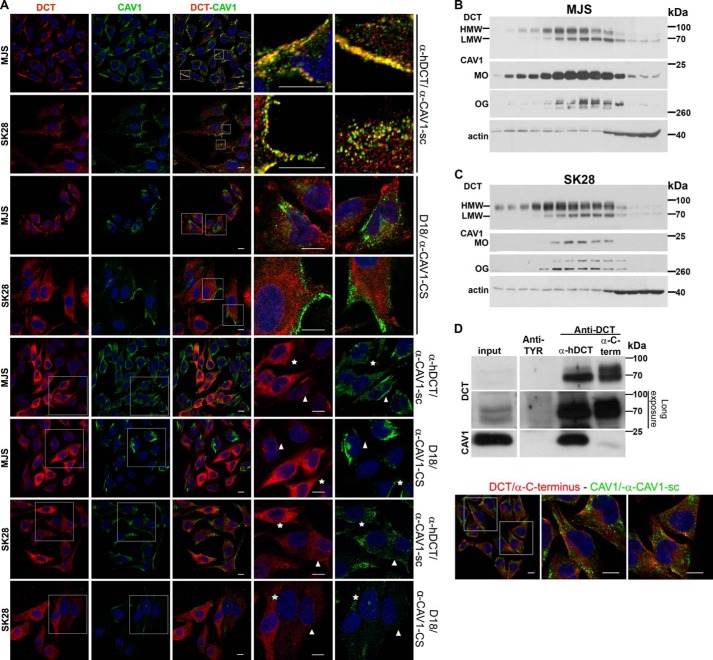
FIGURE 3.
DCT is a constituent of CAV1-associated structures in amelanotic melanoma cell lines. A, DCT and CAV1 distribution in MJS (72 h) and SK28 (96 h) cells by confocal IF microscopy assessed with anti-DCT and anti-CAV1 antibodies. DCT (red) and CAV1 (green) are distributed in common (yellow) (top and 2nd panels) or separate (red or green) structures (3rd and 4th panels) of MJS and SK28 cells. In SK28 cells for CAV1 detection with α-CAV1-CS, increased imaging parameters were used. The incubation with D18 antibody was done overnight in both cell lines. The MJS or SK28 cells overexpressing DCT are indicated by stars, and adjacent cells moderately expressing DCT are indicated by arrowheads. B and C, MJS and SK28 cellular fractions separated in a 4–25% Optiprep gradient ultracentrifugation were assessed for DCT and CAV1 in WB with D18/α-CAV1-CS antisera. CAV1 in SK28 samples is done with the Super Signal Femto enhancing system. D, identification of CAV1 as DCT interactor. The material immunoprecipitated with anti-DCT (α-hDCT or α-C-terminal) or anti-TYR (negative control) antisera from MJS (48 h) cell lysate and eluted from protein A-Sepharose beads analyzed in WB for DCT (D18) and CAV1 (α-CAV1-CS) (left panel) and mass spectrometry (see Table 1) is shown. DCT detection by immunofluorescence microscopy with α-C terminus (right panel) supports the existence of a DCT pool in CAV1-free membranes. The antibody combinations used for DCT/CAV1 detection and cell line are indicated at the right and left side, respectively, of each figure. The last two columns represent enlarged merged details or enlarged separate images. Images were acquired using ×40 oil immersion objective. Scale bar, 10 μm. Each experiment is a representative one of three.